Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO -
 Access statistics
Access statistics
Related links
-
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO
Share
Revista mexicana de astronomía y astrofísica
Print version ISSN 0185-1101
Rev. mex. astron. astrofis vol.44 n.1 Ciudad de México Jan. 2008
Flat central density profiles from scalar field dark matter halos
Argelia Bernal,1,3 Tonatiuh Matos,1,3 and Darío Núñez 2,3
1 Departamento de Física, Centro de Investigación y de Estudios Avanzados del IPN, Apdo. Postal 14–740, 07000 México, D. F., México http://www.fis.cinvestav.mx/~tmatos (abernal@fis.cinvestav.mx, tmatos@fis.cinvestav.mx)
2 Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Apdo. Postal 70–543, 04510 México, D. F., México. On Sabbathicak leave at Max–Planck–Institut für Gravitationsphysik, Albert Einstein Institut, 14476 Golm, Germany (nunez@nuclecu.unam.mx)
3 Part of the Instituto Avanzado de Cosmología (IAC), México.
Received 2006 May 24
Accepted 2008 January 10
RESUMEN
El campo escalar con un potencial cosh se comporta en el régimen lineal justo como la materia oscura fría (CDM). Así, la hipótesis de materia oscura escalar (SFDM) predice la misma formación de estructura que CDM. Los parámetros libres del modelo SFDM se fijan con observaciones cosmológicas. En un trabajo anterior mostramos que con dichos valores, la SFDM se colapsa y forma objetos estables con masa del orden de 1012M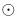 . En este trabajo utilizamos soluciones analíticas para las ecuaciones de Einstein–Klein–Gordon en el caso plano y en el límite de campo débil y mostramos que el perfil de densidad de SFDM corresponde al de una densidad central casi plana y que coincide con el del modelo de CDM en una amplia zona de la región exterior. Este resultado podría resolver el problema de los picos de densidad de CDM sin ninguna hipótesis adicional, lo que apoya la viabilidad del modelo de SFDM.
. En este trabajo utilizamos soluciones analíticas para las ecuaciones de Einstein–Klein–Gordon en el caso plano y en el límite de campo débil y mostramos que el perfil de densidad de SFDM corresponde al de una densidad central casi plana y que coincide con el del modelo de CDM en una amplia zona de la región exterior. Este resultado podría resolver el problema de los picos de densidad de CDM sin ninguna hipótesis adicional, lo que apoya la viabilidad del modelo de SFDM.
ABSTRACT
Scalar fields endowed with a cosh potential behave in the linear regime, exactly as the cold dark matter (CDM) model. Thus, the scalar field dark matter (SFDM) hypothesis predicts the same structure formation as the CDM model. This means that CDM and SFDM are equivalent from the cosmological point of view. The free parameters of the SFDM model are determined by cosmological observations. In previous work we showed that if we use such parameters, the scalar field collapses forming stable objects with a mass around 1012M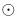 . In the present work we use analytical solutions of the flat and weak field limit of the Einstein–Klein–Gordon equations and show that the SFDM density profile corresponds to a halo with an almost flat central density and that it coincides with the CDM model in a broad outer region. This result could solve the problem of the density cusp DM halo in galaxies without any additional hypothesis, thus supporting the viability of the SFDM model.
. In the present work we use analytical solutions of the flat and weak field limit of the Einstein–Klein–Gordon equations and show that the SFDM density profile corresponds to a halo with an almost flat central density and that it coincides with the CDM model in a broad outer region. This result could solve the problem of the density cusp DM halo in galaxies without any additional hypothesis, thus supporting the viability of the SFDM model.
Key Words: dark matter — galaxies: formation — galaxies: halos
DESCARGAR ARTÍCULO EN FOMATO PDF
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Miguel Alcubierre, Vladimir Ávila Reese, Arturo Ureña and F. Siddhartha Guzmán for many helpful and useful discussions, and Erasmo Gómez and Aurelio Espíritu for technical support. We thank Lidia Rojas for carefull reading and suggestions to improve our work. The numeric computations were carried out in the "Laboratorio de Súper–Cómputo Astrofísico (LaSumA) del Cinvestav". This work was partly supported by Conacyt México, under grants 32138–E,47209–F and 42748 and by grant number I0101/131/07 C–234/07, Instituto Avanzado de Cosmología (IAC) collaboration. Also by the bilateral Mexican–German project DFG–Conacyt 444 MEX–13/17/0–1.
REFERENCES
Alcubierre, M., Becerril, R., Guzmán, F. S., Matos, T., Núñez, D., & Ureña–López, L. A. 2003, Classical Quantum Gravity, 20, 2883 [ Links ]
Alcubierre, M., Guzmán, F. S., Matos, T., Núñez, D., Ureña–López, L. A., & Wiederhold, P. 2002, Classical Quantum Gravity, 19, 5017 [ Links ]
Arbey, A., Lesgourgues, J., & Salati, P. 2001, Phys. Rev. D, 64, 123528 [ Links ]
_________. 2002, Phys. Rev. D, 65, 083514 [ Links ]
Böhmer, C. G., & Harko, T., 2007, J. Cosmol. Astropart Phys., 6, 25 [ Links ]
Guzmán, F. S., & Matos, T. 2000, Classical Quantum Gravity, 17, L9 [ Links ]
Guzmán, F. S., & Ureña–López, L. A. 2004, Phys. Rev. D, 69, 124033 [ Links ]
_________. 2005, in Progress in Dark Matter, ed. J. Val Blain (New York: Nova Science), 39 [ Links ]
Hawley, S. H., & Choptuik, M. W. 2000, Phys. Rev. D, 62, 104024 [ Links ]
Honda, E. P., & Choptuik, M. W. 2002, Phys. Re. D, 65, 084037 [ Links ]
Hu, W., Barkana, R., & Gruzinov, A. 2000, Phys. Rev. Lett., 85, 1158 [ Links ]
Ji, S. U., & Sin, S. J. 1994, Phys. Rev. D, 50, 3655 [ Links ]
Lee, J. W., & Koh, I. G. 1996, Phys. Rev. D, 53, 2236 [ Links ]
MacGaugh, S. S., Rubin, V. C., & de Blok, W. J. G. 2001, AJ, 122, 2381 [ Links ]
Matos, T., & Guzmán, F. S. 2000, Ann. Phys., 9, S133 [ Links ]
_________. 2001, Classical Quantum Gravity, 18, 5055 [ Links ]
Matos, T., Guzmán, F. S., & Núñez, D. 2000, Phys. Rev. D, 62, 061301 [ Links ]
Matos, T., & Ureña–López, L. A. 2000, Classical Quantum Gravity, 17, L75 [ Links ]
_________. 2001, Phys. Rev. D, 63, 063506 [ Links ]
Navarro, J., Frenk, C. S., & White, S. S. M. 1997, Ap J, 490, 493 [ Links ]
Peebles, P. J. E. 2000, Ap J, 534, L127 [ Links ]
Sahni, V., & Wang, L. 2000, Phys. Rev. D, 62, 103517 [ Links ]
Schunck, F. E. 1998, preprint (astro–ph/9802258) [ Links ]
Seidel, E., & Suen, W.–M. 1990, Phys. Rev. D, 42, 384 [ Links ]
_________. 1991, Phys. Rev. Lett., 66, 1659 [ Links ]
_________. 1994, Phys. Rev. Lett., 72, 2516 [ Links ]
Sin, S. J. 1994, Phys. Rev. D, 50, 3650 [ Links ]
Ureña–López, L. A. 2002, Classical Quantum Gravity, 19, 2617 [ Links ]
Ureña–López, L. A., Matos, T., & Becerril, R. 2002, Classical Quantum Gravity, 9, 6259 [ Links ]














