Introduction
ProcamallanusBaylis, 1923, a genus of nematode parasites of freshwater and marine fishes (Moravec, Salgado-Maldonado, & Caspeta-Mandujano, 2000), was originally proposed to include Cucullanus laeviconchus Wedl, 1862, a parasite of freshwater siluriform fishes based on the morphology of the buccal capsule (Baylis, 1923). Olsen (1952) proposed Spirocamallanus for grouping the species that had spiral thickenings in the buccal capsule, whereas Moravec and Sey (1988) considered it as a subgenus of Procamallanus based on the presence of buccal capsule with inner spirals in males and females. Gibbons (2010) has recently considered the latter proposition valid and grouped 6 additional subgenera within Procamallanus .
Neotropical species of Procamallanus belong to the subgenera ProcamallanusBaylis, 1923, Spirocamallanus , and Denticamallanus Moravec and Thatcher, 1997 (Luque, Aguiar, Vieira, Gibson, & Santos, 2011; Moravec, 1998). Luque et al. (2011) listed all 22 species of Procamallanus so far recorded in Brazil. Vaz and Pereira (1934) reported Procamallanus hilarii Vaz and Pereira, 1994, parasitizing the small intestine of Salminus hilarii Valenciennes, 1849 from the Santo Amaro Dam, São Paulo State, Brazil. Later, this was classified in the subgenus Spirocamallanus by presenting oral capsule with inner spirals in both sexes (Moravec & Sey, 1988). This species was redescribed by Pinto and Noronha (1976) and Rodrigues, Pinto, and Noronha (1991); however, in both studies the authors used the original figures of Vaz and Pereira (1934), thereby missing many morphological details, such as cephalic characters and posterior extremity of males.
In Brazil, P . (S .) hilarii was recorded in the states of Ceará in Astyanax bimaculatus (Linnaeus, 1758) and Steindachnerina elegans (Steindachner, 1874) (Pereira, Dias, & Azevedo, 1936), Rio de Janeiro in A. bimaculatus and Astyanax parahybae (Eigenmann, 1908) (Abdallah, Azevedo, & Luque, 2004), São Paulo in A. bimaculatus (Kloss, 1966; Kohn & Fernandes, 1987) and Salminus hilarii Valenciennes, 1850 (Vaz & Pereira, 1934), as well as unidentified minnows (Pinto & Noronha, 1976), Paraná in Astyanax fasciatus (Cuvier, 1819) (Kohn, Fernandes, Pipolo, & Godoy, 1988; Pinto & Noronha, 1976) and unidentified minnows (Pinto & Noronha, 1976), and Rio Grande do Sul in Acestrorhynchus microlepis (Schomburgk, 1841), Astyanax jacuhiensis , Astyanax aff. fasciatus , Hoplias lacerdae Miranda Ribeiro, 1908, Hoplias malabaricus , and Rhamdia quelen (Quoy and Gaimard, 1824) (Kohn, Fernandes, Pipolo, & Godoy, 1989). This nematode also was recorded in Trichomycterus piurae (Eigenmann, 1922) in Peru (Freitas & Ibañez, 1970) and in Astyanax abramis , A. bimaculatus , A. fasciatus , Hoplias malabaricus , Leporinus obtusidens (Valenciennes, 1836), Oligosarcus jenynsii (Günther, 1864), Pimelodus albicans (Valenciennes, 1840), and Salminus brasiliensis (Cuvier, 1816) in Argentina (Ramalho, 1997, 2005). Luque et al. (2011) also cited the characid Oligosarcus macrolepis Steindachner, 1877 as a host of this species, but the collection site was not reported. While Lima et al. (2003) and Buckup, Menezes, and Ghazzi (2007) report that O. macrolepis occurs in the Jequitinhonha river basin in Bahia and Minas Gerais, these states were not surveyed by Luque et al. (2011). Their collections were restricted to the states of Ceará, Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo, Paraná, and Rio Grande do Sul.
Procamallanus (S.) hilarii was recorded in A. aff. fasciatus and A. jacuhiensis by Kohn et al. (1989), but a comparison of its ecological parameters between these host species is missing. The present study aims to fulfill this gap by providing a detailed description of the morphology of P. (S.) hilarii from Lake Guaiba, Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil, and discussing their ecological parameters in light of their trophic relations.
Materials and methods
Seventy specimens of A . aff. fasciatus and 60 of A . jacuhiensis were collected with seine nets between March 2012 and December 2013 from Lake Guaiba, in the municipalities of Guaiba (30°08′28″S, 51°18′53″W) and Barra do Ribeiro (30°17′11″S, 51°18′01″W), State of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Fishes were individually packed in plastic sacks, and transported in ice coolers to the Laboratório de Helmintologia of the Departamento de Zoologia (DZ), Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS) for necropsy. Hosts were determined according to Lucena, Castro, and Bertaco (2013). Nematodes were collected, fixed, and preserved following Amato and Amato (2010). These were temporarily mounted and cleared in Amann's lactophenol (Humason, 1979). En face preparations were mounted in glycerin jelly according to Anderson (1958) to visualize cephalic characters. Specimens were prepared for scanning electron microscopy (SEM) through dehydration in ethanol (70° to 100° GL) and the ethanol was gradually replaced by acetone (10-100%) to critical point dried. Then, they were mounted on stubs, coated with carbon and gold, and examined in a JEOL JSM 6060 at Centro de Microscopia Eletrônica (CME) at UFRGS.
Measurements are shown in micrometers (μm) unless otherwise stated. The parameters reported are the range followed by mean ± standard deviation, and sample size is between parentheses. Photomicrographs were taken with a Zeiss Axiolab microscope with phase contrast. Line drawings were made with a drawing tube mounted on a Nikon E-200 microscope, scanned and prepared using CorelDraw X4(r) and Adobe's Photoshop(r) CS2. Ecological parameters follow Bush, Lafferty, Lotz, and Shostak (1997). Voucher helminth specimens were deposited in the 'Coleção Helmintológica do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz' (CHIOC), Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil. Voucher host specimens were deposited in the 'Coleção Ictiológica', DZ/UFRGS. The Z -test was used to compare prevalence data between the host species, whereas median intensity and median abundance of infection were compared by the Student t test (Zar, 2010).
Description
Procamallanus (Spirocamallanus) hilariiVaz and Pereira, 1934 (Figs. 1-18)
Diagnosis (based on 15 males and 15 females mounted in lactophenol, 2 en face, and 5 males prepared for scanning electron microscopy ). Spiruroidea, Camallanidae. Reddish nematodes in life, with transverse cuticular striations. Oval mouth opening surrounded by 6 elevations (1 ventral, 1 dorsal, and 4 lateral), and 8 papillae distributed in 2 circles (4 internal smaller and 4 external larger) (Figs. 2, 8, 9 and 16). Yellowish brown buccal capsule, sclerotized, with 13-16 internal spirals, continuous, some incomplete (Figs. 1, 7, 15 and 16). Basal ring sclerotized between buccal capsule and muscular esophagus (Figs. 1 and 7). Esophagus divided into a shorter muscular and a longer glandular portion (Figs. 1 and 7). Nerve ring anterior to deirids and excretory pore (Figs. 1, 7, 15 and 17). Males (N = 15). Body 6.34-9.07 mm (7.58 ± 0.89 mm; N = 15) long, 0.16-0.22 mm (0.18 ± 0.02 mm; N = 15) wide. Buccal capsule 45.00-70.00 (53.17 ± 5.71; N = 15) long, 52.50-65.00 (56.67 ± 3.74; N = 15) wide, with 13-16 internal spirals. Basal ring 7.50-12.50 (9.67 ± 1.30; N = 15) long, 20.00-40.00 (32.50 ± 4.82; N = 15) wide. Muscular esophagus 340.00-460.00 (390.00 ± 34.11; N = 15) long, 50-70 (59.67 ± 5.50; N = 15) and 100-130 (113.33 ± 10.47; N = 15) wide in the anterior and posterior ends, respectively; glandular esophagus 1.04-1.77 mm (1.40 ± 0.20 mm; N = 15) long, 0.09-0.14 mm (0.11 ± 0.01 mm; N = 15) wide. Esophagus representing 24% of total body length (TBL), and muscular portion corresponding to 28% of the glandular portion. Nerve ring 162.50-222.50 (195.83 ± 16.63; N = 15) from anterior extremity. Deirids 185.00-282.50 (235.00 ± 24.68; N = 12) from anterior extremity. Excretory pore 215.00-352.50 (279.17 ± 36.37; N = 15) from anterior extremity. Posterior end of the body with 8 pairs of papillae: 4 pre- and 4 post-cloacal (Figs. 3, 10 and 18). Similar spicules, bifurcated distal end, with length of 52.50-77.50 (64.83 ± 5.94; N = 15) and 62.5-87.5 (72.83 ± 6.54; N = 15) (Figs. 3, 4, 10 and 11). Gubernaculum absent. Cloaca 120.00-200.00 (162.83 ± 25.03; n = 15) from the posterior extremity, pointed tail (Figs. 3, 10 and 18). Females (N = 15). Body 12.92-18.78 mm (15.69 ± 1.93 mm; N = 15) long, 0.22-0.44 mm (0.34 ± 0.06 mm; N = 15) wide. Buccal capsule 55.00-65.00 (60.00 ± 3.13; N = 15) long, 60.00-72.50 (66.67 ± 3.62; N = 15) wide, with 13-16 internal spirals. Basal ring 7.50-12.50 (10.67 ± 1.48; N = 15) long, 35.00-45.00 (39.67 ± 2.81; N = 15) wide. Muscular esophagus 370.00-520.00 (434.00 ± 36.41; N = 15) long, 60.00-80.00 (69.33 ± 4.58; n = 15) and 120.00-150.00 (128.67 ± 9.9; n = 15) wide in the anterior and posterior ends, respectively; glandular esophagus 1.15-2.22 mm (1.77 ± 0.26 mm; N = 15) long, 0.12-0.17 mm (0.14 ± 0.01 mm; N = 15) wide. Esophagus representing 11% of TBL, and muscular portion corresponding to 25% of the glandular portion. Nerve ring 182.50-232.50 (207.17 ± 14.48; N = 15) from anterior extremity. Deirids 250.00-350.00 (285.77 ± 34.86; N = 13) from anterior extremity. Excretory pore 280.00-410.00 (341.04 ± 47.07; N = 12) from anterior extremity. Vulva post-equatorial, 5.48-7.94 mm (6.82 ± 0.76 mm; N = 15) from posterior extremity (Figs. 5 and 12). Eggs 7.50-10.00 (9.00 ± 1.29) long and 5.00 to 10.00 (7.50 ± 1.67) wide (N = 10), with first larval stage 390.00-529.50 (514.97 ± 60.38; N = 15) long and 25.00-32.50 (27.00 ± 3.02; N = 15) wide (Figs. 12, 13 and 14). Anus 80.00-140.00 (111.33 ± 16.42; N = 15) from posterior extremity, pointed tail (Figs. 6 and 13).

Figures 1–6 Incomplete diagrams of Procamallanus (Spirocamallanus) hilarii. (1), Anterior extremity of males. Scale bar=150μm; (2), en face view. Scale bar=50μm; (3), posterior extremity of males. Scale bar=50μm; (4), detail of the ventral view of the spicules. Scale bar=50μm; (5), vulvar region of females. Scale bar=100μm; (6), posterior extremity of a young female. Scale bar=150μm.

Figures 7–11 Photomicrographies of males of Procamallanus (Spirocamallanus) hilarii. (7), Anterior extremity in phase contrast. Scale bar=100μm; (8), en face view showing the 6 cuticular elevations (white arrow heads). Scale bar=50μm; (9), en face view showing the 4 outer papillae (white arrow heads), amphids (black arrow heads) and the end of the buccal capsule (asterisk). Scale bar=50μm; (10), posterior extremity showing the spicules (black arrow heads). Scale bar=50μm; (11), detail of the ventral view of the spicules showing the distal bifurcation (white arrow heads). Scale bar=50μm.
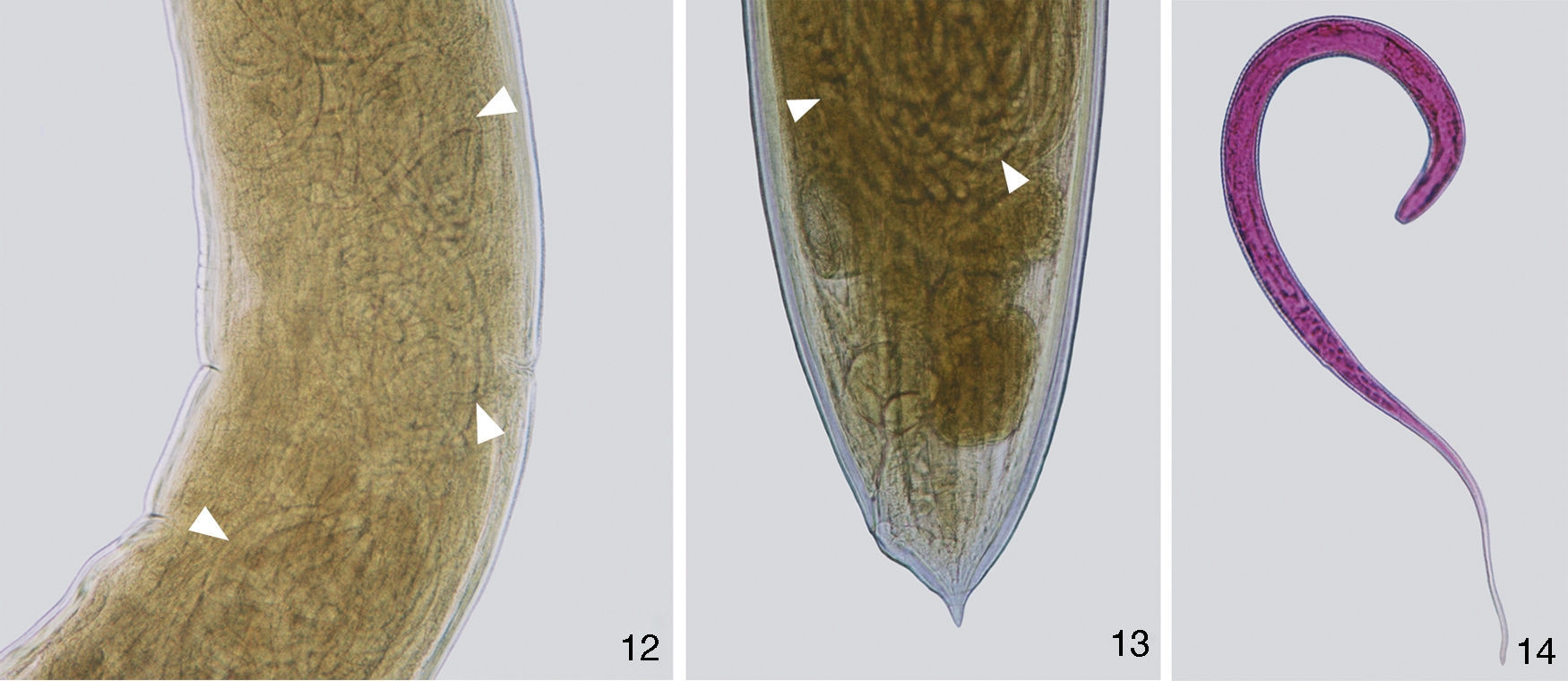
Figures 12–14 Photomicrographies of females of Procamallanus (Spirocamallanus) hilarii. (12), Vulvar region with larvae L1 (white arrow heads). Scale bar=250μm; (13), posterior extremity of a gravid female showing larvae L1 (white arrow heads). Scale bar=100μm; (14), larvae stained with rose bengal. Scale bar=100μm.

Figures 15–18 Scanning electron microscopy of Procamallanus (Spirocamallanus) hilarii. (15), Anterior extremity with deirid (black arrow head) and excretory pore (white arrow head). Scale bar=50μm; (16), detail of the anterior extremity showing cuticular elevations (asterisks), inner papillae (black arrow heads), outer papillae (white arrow heads) and amphids (black arrows). Scale bar=10μm; (17), detail of the deirid. Scale bar=10μm; (18), posterior extremity of a male showing the phasmids (white head arrows). Scale bar=20μm.
Taxonomic summary
Synonyms: Procamallanus cearensisPereira, Dias and Azevedo, 1936; Spirocamallanus incarocaiFreitas & Ibañez, 1970.
Hosts : A. aff . fasciatus and A. jacuhiensis .
Host specimens deposited. A. aff. fasciatus : UFRGS 19121 (male); UFRGS 19122 (female) and A. jacuhiensis : UFRGS 19123 (male); UFRGS 19124 (female).
Localities: Lake Guaíba, Municipalities of Guaíba and Barra do Ribeiro, State of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
Site of infection: stomach and intestine.
Voucher specimens deposited : CHIOC n° 35948.
Ecological parameters: the prevalence of P. (S.) hilarii in A. aff. fasciatus (69%) was higher than in A. jacuhiensis (18%) (Z = 5.7355, ptwo-tailed < 0.0001; Table 1). However, the mean intensity (A. aff. fasciatus = 2 helminths/host vs. A. jacuhiensis = 5 helminths/host; t = −0.87, df = 10, p = 0.4) and the mean abundance (A. aff. fasciatus = 1.6 helminths/host vs. A. jacuhiensis = 0.9 helminths/host; t = 1.24, df = 70, p = 0.22) of infection were similar between species (Table 1).
Table 1 Ecological parameters of Procamallanus (Spirocamallanus) hilarii populations and feeding habits of host species.
| Host | N host | Diet | Prevalence (%) | Mean intensity (helminths/host) | Mean abundance (helminths/host) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astyanax abramis | 228 | Juveniles: vegetal matter and insects. Adults: microcrustaceans, crustaceans and insectsa | 52 | 3 | - | Ramalho (2005) |
| Astyanax bimaculatus | 124 | Vegetal matter, insects and other animals (spiders and fish rests)b | 45 | 3 | - | Ramalho (2005) |
| 37 | 40 | 2 | - | Ramalho (2005) | ||
| 23 | 4 | - | - | Kohn and Fernandes (1987) | ||
| 40 | 3 | 1 | <0.1 | Abdallah et al. (2004) | ||
| Astyanax fasciatus | 412 | Vegetal matter, insects and some microcrustaceansc | 56 | 2 | - | Ramalho (2005) |
| 16 | 6 | 1 | 0.1 | Kohn et al. (1988) | ||
| Astyanax aff. fasciatus | 70 | Vegetal matter, insects and some microcrustaceansc | 69 | 2 | 1.6 | Present study |
| 8 | 25 | 1 | 0.3 | Kohn et al. (1989) | ||
| Astyanax jacuhiensis | 17 | Vegetal matter and insectsc | 65 | 2 | 1.2 | Kohn et al. (1989) |
| 60 | 18 | 5 | 0.9 | Present study | ||
| Astyanax parahybae | 40 | * | 5 | 1 | 0.1 | Abdallah et al. (2004) |
| Acestrorhamphus macrolepis | 11 | * | 45 | 3 | 1.4 | Kohn et al. (1989) |
| Hoplias lacerdae | 3 | Adults: fishd | 33 | 1 | 0.3 | Kohn et al. (1989) |
| Hoplias malabaricus | 6 | Juveniles: insects and crustaceans. Adults: fish and shrimpe | 17 | 2 | 0.2 | Kohn et al. (1989) |
| Rhamdia quelen | 8 | Fish, molluscs, crustaceans and insectse | 12 | 2 | 0.1 | Kohn et al. (1989) |
b Andrian, Silva, and Peretti (2001).
* Unknown data.
Remarks
The nematodes found in the stomach and in the anterior and middle portions of the small intestine of A. aff. fasciatus and A. jacuhiensis were identified as P. (S.) hilarii based on the taxonomic keys proposed by Rodrigues et al. (1991) and Moravec (1998) by presenting an oral capsule with inner spirals in both sexes and a glandular esophagus at least 3 times longer than the muscular esophagus.
Species of Procamallanus have 6 elevations distributed over the anterior region of the buccal capsule, 8 papillae arranged in 2 circles, and a pair of lateral amphids (Moravec, 1998). Unlike the round oral opening reported for P. (S.) hilarii by Moravec (1998), the specimens examined presented an oval oral opening. Ramalho (1997) cited the presence of 3 pairs of small cephalic papillae, 1 lateral and 2 median. In fact, these papillae are the cuticular elevations described by Moravec (1998) and observed in the present study (Figs. 2, 8, 9 and 16).
Morphological differences also were found in the posterior end of males. In species considered synonymous of P. (S.) hilarii , P. cearensis and S. incarocai , Pereira et al. (1936) and Freitas and Ibañez (1970) mentioned the presence of thin caudal alae, whereas Rodrigues et al. (1991) and Moravec (1998) noted the absence of caudal alae as reported in the present study (Figs. 3, 10 and 18). Freitas and Ibañez (1970) and Ramalho (1997) described 8 pairs of pedunculate papillae, unlike the sessile papillae reported here (Figs. 3, 10 and 18) and in Pereira et al. (1936), Rodrigues et al. (1991), and Moravec (1998). Additionally, although the spicules of the specimens examined in the present study are similar to those described by Pereira et al. (1936), these authors did not report the bifurcation of its distal end. In general, the dimensions of characters were similar to those reported in the literature (Freitas & Ibañez, 1970; Pereira et al., 1936; Pinto & Noronha, 1976; Ramalho, 1997; Rodrigues et al., 1991; Vaz & Pereira, 1934). Male and female body size was an exception. The total length of males and females reported in this study was higher. Only Freitas and Ibañez (1970) reported larger females. These authors also reported that the vulva is closer (2.4 mm) to the posterior end of the worm. Morphological differences may result from intraspecific variations in length, for example, or from difficulties in visualizing structures, as was the case for the caudal papillae and caudal alae. However, the MEV images clarify these discrepancies.
Ecological parameters of P. (S.) hilarii populations vary among host species and study (Table 1). For instance, prevalence ranges from 3% in A. bimaculatus to 69% in A. aff. fasciatus . These differences suggest that the definitive hosts exploit a variable diet in different environments. In the case of the present study, the differences in prevalence of P. (S.) hilarii between the 2 characid hosts likely reflect the differences in their feeding habits. Since the life cycle of Procamallanus spp. includes copepods as intermediate hosts (Anderson, 2000), it is possible to suggest that these small crustaceans are more heavily preyed upon by A. aff. fasciatus than by A. jacuhiensis . It is also interesting that the intensity of infection showed the opposite pattern, being higher in A. jacuhiensis , a species with a more herbivorous diet (Villela, Becker, & Hartz, 2002). Together, the data on prevalence and intensity of infection may suggest that the fewer A. jacuhiensis individuals that feed on copepods do that at a higher frequency than most A. aff. fasciatus . In addition, variations in environmental characteristics can be related to the availability in the environment of infected copepods.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dra. Ana P. S. Dufech for field assistance, Dr. Philip J. Scholl for reviewing the English, and Centro de Microscopia Eletrônica (UFRGS) for SEM preparations. MG also thanks the Brazilian National Research Council (CNPq) for financial support (process #131068/2012-1) and CCM thanks the Brazilian Higher Education Authority (CAPES) and the Research Foundation of the State of Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS) for post-doctoral fellowships (PNPD/CAPES 2010).











 nueva página del texto (beta)
nueva página del texto (beta)


