Introduction
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TTC) is also referred to as ‘transient apical ballooning’, stress cardiomyopathy, ‘broken heart’ syndrome or neurogenic stunned myocardium, is a recently recognized acute cardiac disease entity. The term takotsubo (tako = octopus, tsubo = a pot) was introduced by Sato and Dote in 1990 and 1991.1,2
Since its first description in Japan, takotsubo (stress) cardiomyopathy has gained worldwide recognition. Occurs mostly in postmenopausal women with or without cardiovascular disease, and is commonly associated with emotional or physical stress.3
Treatment of takotsubo cardiomyopathy usually requires only supportive care in the acute stage because a reversal of the syndrome occurs without treatment. The prognosis is generally favorable including cardiogenic shock. However, after nearly 27 years of extensive efforts toward a better understanding of this disorder, current knowledge remains limited.4,5
Last September 19, 2017 a 7.1 Richter magnitude earth- quake killed more than 300 people in Mexico City and toppled dozens of buildings. Many people suffer post- traumatic stress and this situation can be associated to stress cardiomyopathy. It is important for all involved clinicians to recognize the diagnosis and possess knowledge about the evaluation of these affected patients. We presented the case report of a female who suffer stress related with earthquake and arrived to emergency department presenting cardiogenic shock.
Case report
A 79-year-old postmenopausal female presented to the emergency department (ED) with a chief complaint of chest tightness. The patient reported high intensity oppressive thoracic pain, with irradiation to the back, associated with nausea, vomiting, and diaphoresis. On the previous 15 h, the patient was rescued under the rubble that fell on her body, being the victim of the earthquake of September 19, 2017, in Mexico City. The patient’s past medical history included hypertension and dyslipidemia. Medications upon admission included, valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide 80/12.5 mg daily. Cardiovascular risk factors were: age, stress, dyslipidemia and hypertension.
Upon presentation, the patient had 53 mmHg of systolic BP (blood pressure) and 22 mmHg of diastolic BP, heart rate 85 beats/min, oxygen saturation 82%, weight 60 kg. Initial cardiac markers were elevated with mioglobine 133.3 ng/ml (17.4---105.7), creatine phosphokinase (CPK) muscle and
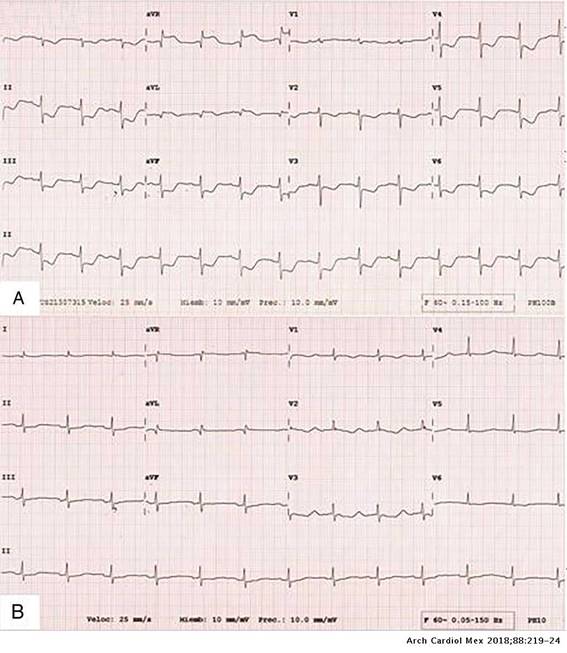
Figure 1: (A) Electrocardiogram results showed normal sinus rhythm, ST elevation in aVR, DI and aVL, and minimal ST depression in the rest of the leads. (B) Electrocardiogram after cardiac catheterization is normal.
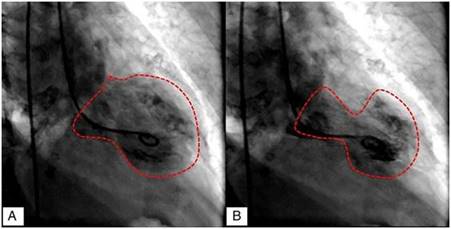
Figure 2: Cardiac catheterization demonstrating left ventriculography in diastole (A), and ‘‘apical ballooning’’ in systole (B).
brain (MB) 13.4 ng/ml (0---4), and Troponin-I 3.77 ng/ml (<0.04). Electrocardiogram results showed normal sinus rhythm, ST elevation in aVR, I and aVL, and minimal ST depression in the rest of the leads (Fig. 1). The patient immediately had cardiac catheterization with left ventriculography. The cardiac catherization revealed non-dominant right coronary without lesions, short left main coronary artery without lesions, left anterior descending artery with- out lesions, dominant left circumflex artery without lesions, 40% plaque in proximal posterolateral artery. The ventriculography report apical ballooning (Fig. 2). The echocardiogram showed left ventricular apical anterior, apical inferior, apical lateral and apical septum segments were akinetic,with compensatory hyperkinesis of all basal portions, an estimated left ventricular ejection fraction of 30% and severe mitral regurgitation (Fig. 3). She was admitted to the coronary unit, where the patient received mechanical invasive ventilation which retired on the second day, she was in cardiogenic shock with hypotension: 47 mmHg of systolic BP and 51 mmHg of diastolic BP mmHg, hypothermic T 35 ◦C, treated with norepinephrine, vasopressin and levosimendan, which were removed on the second day. On the third day, the electrocardiogram of control was normal, echocardiogram with minimal apical hypokinetic, the rest of the left ventricular segments were normal, ejection fraction of 60% and CPK 501 U/l, CPK MB 13 ng/ml, Troponin-I
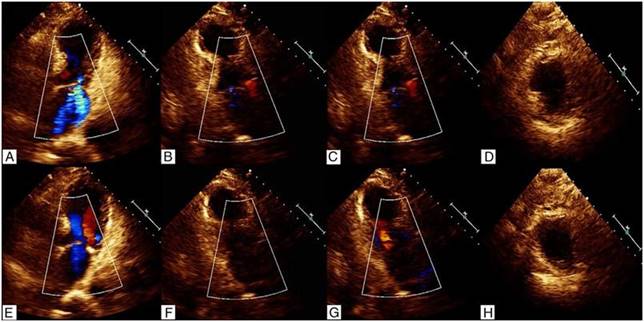
Figure 3: The echocardiogram showend left ventricular apical anterior, apical inferior, apical lateral and apical septum segments were akinetic.
14.15 ng/ml. She was successfully discharged from the hospital.
Discussion
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy has been observed worldwide, although initially reported in Japan. The prevalence is underestimated, the reported frequency of TTC in patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome that has been reported in larger studies has been reported to be between 1.7% and 2.5%, and about 0.02% of all hospitalizations in the United States (up to 10% if only women are considered).6,7 The incidence of primary TTC increased from 2.3 to 7.1 per 100,000 person year and increased almost 20 times from 2006 to 2012.8,9
TCC has a striking female postmenopausal predominance, in more than 80% of cases in various reports and with mean age of 62---76 years, although it has also been observed in women under the age of 50 (5---11% of cases), and premenopausal women.1,10,11 As this case, the patient often has cardiovascular comorbidities such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, and smoking, making the clinical profile similar to patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Also, has been report a higher frequency of comorbid psychiatric disorders such as anxiety, depression and substance abuse.1,5,12,13 The pathophysiology of TTC is complex and may be multifactorial. The main proposed mechanisms are myocardial ischemia, epinephrine-induced switch in signal trafficking, blood-borne catecholamine myocardial toxicity, left ventricular outlet tract obstruction (LVOTO), and autonomics nervous system dysfunction with sympathetic nervous system hyperactivation including local cardiac sympathetic disruption and norepinephrine seethe and spillover.3,6,14
Takotsubo syndrome is classified as both a primary and an acquired cardiomyopathy by the AHA, and as an unclassified cardiomyopathy by the ESC.15,16 The etiology of TTC remains uncertain and it is likely that multiple factors are involved. A characteristic feature of the syndrome is its association with an identifiable stressful event, ranging from what may be considered an emotionally stressful event with- out a physical component to a physical stressor, although in up to one-third of patients, no trigger can be identified. The emotional distress and chest pain after the earthquakes as this case were diagnosed in Niigata, Japan in 2004, earth- quakes in Christchurch, New Zealand, in 2010 and 2011 and in the USA in 2011 during Hurricane Irene, the worst tornado outbreak to hit the USA to date.1,2,5,6,17-20 The 2017 cen- tral Mexico earthquake struck at 13:14 CDT on September 19, 2017 with a magnitude estimated to be 7.1 and strong shaking for about 20 s. Many people after an earthquake are sometimes dismissed or managed with benzodiazepines and physiological consult. While emotional support needed for survivors after an earthquake, also these victims should be in the emergency department.
The most common symptoms at presentation are chest pain (70%) and dyspnea (20%). The symptoms and signs are similar to those seen in other acute cardiac conditions characterized by acute myocardial ischemia or heart failure, such as ACS and myocarditis, and hence do nothelp in the differential diagnoses. TTC can also present as cardiac arrest, cardiogenic shock, syncope and pulmonary edema, and serious ventricular arrhythmias occur more rarely in patients with TTC.14 The most frequent findingon the admission ECG is ST-segment elevation, which most often occurs in the precordial leads in up to 56% and 39% had T wave inversion and the remaining had QT prolongation or pathological Q waves. Arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation and Torsade de pointes have also been reported. It is challenging to distinguish TTC from an ACS on the basis of the ECG alone; therefore, access to emergency coronary angiography should not be delayed. Resolution of ECG abnormalities is frequently seen after a couple of months.3,21-23 Cardiac enzymes such as CPK and Troponin-I assays are typically only mildly elevated. The levels of brain natriuretic pep- tide (BNP), however, tend to be higher in TTC compared with acute coronary syndrome.1-5 Coronary angiography may be completely normal, but the presence of CAD does not preclude a diagnosis of TTC. The typical wall motion abnormalities of TTC are clearly demonstrated on left ventriculography. The classic pattern of hypokinesis, akinesis or dyskinesis of the apical and mid-ventricular segments, extending beyond a single epicardial coronary distribution, is perhaps one of the most helpful diagnostic features. There are four types of takotsubo cardiomyopathy; Among the 1750 study patients, the most common type of takotsubo (stress) cardiomyopathy was the apical type (in 81.7% of patients), followed by the midventricular type (in 14.6% of patients), the basal type (in 2.2% of patients), and the focal type (in 1.5% of patients).1,2,4,5,22 Echocardiography is particularly useful in identifying systolic anterior motion (SAM) of the mitral valve leaflets in those with a hyperkinetic basal LV (left ventricular), or acute mitral regurgitation, or determining the estimated pulmonary artery pressure, all of which have been related to in-hospital mortality. Repeat echocardiography is use- ful (and recommended) to demonstrate recovery of LV function.4
Diagnostic criteria for takotsubo syndrome have been proposed from several centers (for example: Gothenberg (Sweden), Italina network (Italy), MRI-based (USA and Europe) and Mayo Clinic (USA)), using various diagnostic references. The Mayo Clinic diagnostic criteria were originally proposed in 2004 and subsequently modified in 2008 and are the most widely used in clinical practice and research: Transient hypokinesis, akinesis, or dyskinesis of the left ventricular mid-segments with or without apical involvement; the regional wall motion abnormalities extend beyond a single epicardial vascular distribution; a stressful trigger is often, but not always present. Absence of obstruc- tive coronary disease or angiographic evidence of acute plaque rupture.New electrocardiographic abnormalities (either ST-segment elevation and/or T-wave inversion) or modest elevation in cardiac troponin. Absence of pheochro- mocytoma and myocarditis.6,7
Treatment of the precipitating and predisposing diseases: in almost one-third of the patients, TTC is triggered by physical stress and emotional stress. Treatment during the acute stage should be supportive and focus on appropriate treatment of complications, in mild cases, beta-blockers and aspirin may be considered, in cases complicated byheart failure, conventional treatment. In patients with extensive midapical ballooning and documented thrombus in the left ventricle or embolic complications, anticoag- ulation is recommended for 2---3 months. Treatment of cardiogenic shock is an important and life-threatening complication in TTC. The crucial step in treatment is to detect whether the hypotension is caused by LVOTO with SAM and mitral regurgitation or primary pump failure. Catecholamine inotropics such as adrenaline and nora- drenaline, dopamine, milrinone, and isoproterenol are contraindicated. Treatment with diuretics, nitroglycerine, and an intraaortic balloon pump should be avoided because of the risk of aggravation of LVOTO. The suggested treat- ment is intravenous fluid and parenteral beta-blockers, phenylphrine. In primary pump failure, treatment with venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or a left ventricular assist device should be considered as a bridge to recovery. Non-catecholamine inotropics such as levosimendan may also be considered in primary pump failure in TTC but catecholamine-based inotropics should be avoided. Treatment after discharge: Observational studies have shown that the use of ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers was associated with improved survival up to 1 year after the acute event. We found no study that looked at the medical management of physical symptoms of these survivors. Increased awareness of this entity will con- tribute to timely diagnoses and appropriate treatment.5,6,14 The prognosis of TTC was initially thought to be benign. Subsequent series, however, have demonstrated that both short-term mortality and long-term mortality are higher than previously recognized. The prevalence of prehospital mortality is unknown, but should not be underestimated, as mortality during the acute phase in hospitalized patients is 4-5%, which is similar to the mortality seen in patients with STEMI.2,8,21,24
Conclusion
Takotsubo syndrome is a cardiomyopathy reported for
27 years, however, a worldwide consensus has not been established for diagnosis, and the Mayo Clinic diagnostic criteria are the most widely used in clinical practice and research, pathophysiology is complex and may be multifactorial. The etiology of takotsubo cardiomyopathy remains uncertain and it is likely that multiple factors are involved. We report a case of a postmenopausal woman who, after the earthquake, arrived to ED, had a cardiogenic shock secondary to Takotsubo syndrome with early diagnosis and adequate response to treatment during the acute stage.











 nova página do texto(beta)
nova página do texto(beta)


