Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Acessos
Acessos
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
Computación y Sistemas
versão On-line ISSN 2007-9737versão impressa ISSN 1405-5546
Comp. y Sist. vol.10 no.2 Ciudad de México Out./Dez. 2006
Comparación de Cuatro Algoritmos que dan Solución Numérica a la Deconvolución en Sistemas Monodimensionales
A Comparative Evaluation of four Algorithms for Numeric Solution of the Deconvolution on Unidimensional Systems
José I. De la Rosa Vargas, Gerardo Miramontes de León, Ernesto García Domínguez, Maria A. Esquivel, y Jesús Villa Hernández
Laboratorio de Procesamiento Digital de Señales Universidad Autónoma de Zacatecas (UAZ) Av. López Velarde, Zacatecas, Zac., C.P. 98064 ismaelrv@ieee.org ; gmiram@ieee.org ; egarcia@uaz.edu.mx ; araizama@uaz.edu.mx ; y jvillah@uaz.edu.mx
Article received on September 15, 2004
Accepted on February 02, 2007
Resumen
En el presente trabajo se presenta la comparación de un algoritmo de deconvolución con respecto de otros tres algoritmos clásicos utilizados para deconvolución unidimensional de señales. El algoritmo fue propuesto y analizado en el laboratorio de procesamiento digital de señales de la UAZ. Durante las últimas tres décadas se han desarrollado nuevas ideas sobre soluciones a problemas de deconvolución o restauración de señales n–dimensiónales, la idea sigue siendo la misma que se plantea en la literatura de la ingeniería que data de los años 50s "restaurar señales o aproximarlas a su forma original para realizar un análisis de las mismas con errores relativamente pequeños". Cuando una señal x(t) se origina tiene que pasar por algún medio para poder ser captada, durante este proceso se realiza una operación llamada convolución entre x(t) y otro tipo de señales, en el momento en que captamos la señal, ésta ya no es x(t) sino la convolución de x(t) con una función h(t) mas componentes de ruido existentes en el medio. Para obtener la señal x(t) es necesario resolver un problema inverso el cual al final nos proporciona una estimación de x(t) o 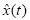 . El propósito final del trabajo es evaluar y clasificar la capacidad de restauración de señales de cada uno de los cuatro métodos.
. El propósito final del trabajo es evaluar y clasificar la capacidad de restauración de señales de cada uno de los cuatro métodos.
Palabras clave: Deconvolución, Problema Inverso, Análisis Homomórfico, Iterativo.
Abstract
The present paper presents the comparison of a deconvolution algorithm with other three classical approaches for one–dimensional deconvolution of signals. The algorithm was proposed at the digital signal processing laboratory at UAZ. During the last three decades, the development of new ideas on the solution about deconvolution or n–dimensional signal restoration methods, have become to a new meaning to this problem, the idea remains the same since the 50's in the engineering literature, that is " signal restoration or approximation to it's original form with the purpose of a better analysis ". When a signal x(t) is generated, the only way to be picked up is by a sensor. During the sensing process the convolution of x(t) with another type of signals occurs. Then, a new signal is generated by the convolution of x(t) with a function h(t) and other noisy components. To obtain the original signal x(t), we have an inverse problem and the solution will deliver an estimation of x(t) or 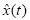 . The final purpose of this work is to evaluate and classify the signal restoration capacity of each method.
. The final purpose of this work is to evaluate and classify the signal restoration capacity of each method.
Keywords: Deconvolution, Inverse Problem, Homomorphic Analysis, Iterative Procedure.
DESCARGAR ARTÍCULO EN FORMATO PDF
Referencias
1. Bandzuch P., Morhác M., and Kristiak J., "Study of the Van Cittert and Gold Iterative Methods of Deconvolution and their Application in the Deconvolution of Experimental Spectra of Positron Annihilation," Elsevier Science Publishers B. V., Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, North–Holland, Section A, 1997, pp. 506–515. [ Links ]
2. Bogert B.P., Healy M. J., and Tukey J.W., "The Quefrency Analysis of Time Series for Echoes: Cepstrum, Pseudo–autocovariance, Cross–cepstrum and Saphe cracking," In Time Series Analysis, M. Rosenblatt, Ed. New York: Wiley, 1963, Chap. 15, pp. 209–243. [ Links ]
3. Castleman K. R., "Digital Image Processing," NJ, Prentice–Hall, Chap. 16, 1996, pp. 387–430. [ Links ]
4. Crilly P. B., "A Quantitative Evaluation of Various Iterative Deconvolution Algorithms," IEEE Trans. on Instrumentation and Measurement, Vol. 40, June 1991, pp. 558–562. [ Links ]
5. Demoment G., "Déconvolution des Signaux," Cours, École Supérieure D'Électricité SUPELEC, 1987–1997, Chap. 5, pp. 51–76. [ Links ]
6. De la Rosa J. I., "Evaluación Comparativa de Cuatro Algoritmos que dan Solución numérica a la Deconvolución de sistemas monodimensionales," Tesis de Maestría, Instituto Politécnico Nacional, CITEDI, 1998. [ Links ]
7. García J., and De la Rosa J. I., "El Cepstrum y un Esquema Simple para Deconvolución," CIE'97 CINVESTAV–IPN, Vol. 2, Septiembre 1997, pp. 329–334. [ Links ]
8. García E., Vega H., Miramontes G., and McBride L. "Noniterative Unfolding Algorithm for Neutron Spectrum Measurements with Bonner Spheres," IEEE Trans. On Nuclear Science, No. 6, Vol. 46. 1999. [ Links ]
9. Gonzales R. C., and Wintz P., "Digital Image Processing," Addison Wesley, Chap. 5, 1989, pp. 205–253. [ Links ]
10. Hua Y., and Sarkar T. K., "Matrix Pencil and System Poles," Elsevier Science Publishers B. V., Signal Proc. 21, 1990, pp. 195–198. [ Links ]
11. Jain A. K., "Fundamentals of Digital Image Processing," NJ, Prentice–Hall, 1989, Chap. 8, pp. 267–341. [ Links ]
12. Jansson P. A., "Deconvolution with Applications in Spectroscopy," Academic Press, 1984, Chap. 3, 4, 7, pp. 69–91, 96–132, 188–225. [ Links ]
13. Lee G.–K., Gelfand S. B., and Fitz M. P., "Bayesian Decision Feedback Techniques for Deconvolution," IEEE Journal on Selected areas of Commun., Vol. 13, No. 1, January 1995, pp. 155–165. [ Links ]
14. Martínez C. A., "Conception D'une Architecture de Processeur de signal VLSI, Programmable en Langage Évolé et Optimale dans le Traitement D'algorithmes Rapides," These de Docteur en Science, Université de Paris–Sud Centre D'Orsay et École Supérieure D'Électricité, 1988, Chap. 2,5, pp. 28–33, 107–113. [ Links ]
15. McBride L. E., Schaefgen H. W., and Steiglitz K., "Time–Domain Approximation by Iterative Methods," IEEE Trans. on Circuit Theory, Vol. CT–13, December 1966, pp. 381–387. [ Links ]
16. Miramontes G., McBride L. E., and García E., "Deconvolution with Noise as System Identification," IEEE Workshop on Emerging Technologies, Inteligent Measurement and Virtual Systems for Instrumentation and Measurements – ETIMVIS'98 St. Paul, MN, USA May 15 –16, 1998. [ Links ]
17. Oppenheim A. V., "Superposition in a Class of Nonlinear Systems," Tech. Rep. 432, Res. Lab. Electron., M.I.T., Cambridge, MA, March 31, 1965. [ Links ]
18. Oppenheim A. V., and Schafer R. W., "Digital Signal Processing," NJ, Prentice–Hall, 1975. [ Links ]
19. Oppenheim A. V., and Schafer R. W., "Discrete–Time Signal Processing," NJ, Prentice–Hall, 1989, Chap. 12, pp. 768–826. [ Links ]
20. Steiglitz K., and McBride L. E., "A Technique for Identification of Linear Systems," IEEE Trans. Auto. Contr., Vol. AC–10, 1965, pp. 461–464. [ Links ]
21. Twomey S., "On the Numerical Solution of Fredholm Integral Equations of First Kind by the Inversion of Linear System Produced by Quadrature," Journal Asso. Comp. Mach., Vol. 10, 1962, pp. 97–101. [ Links ]
22. Van Cittert P. H.,"Zum Einfluss der Spaltbreite auf die Intensitatswerteilung in Spektrallinien II," Z. Phys. Vol. 69, 1931, pp. 298–308. [ Links ]














