1. Introduction
The importance of invertebrate traces in paleontology, sedimentology, and stratigraphy has been demonstrated in several works (Pembertonet al., 2000, 2002; MacEachernet al., 2007, 2012). A remarkable characteristic of trace fossils is the amount of information that can provide concerning sedimentary environments (MacEachernet al., 2012). These biogenic structures give evidence of energy, sediment grain size, substrate type and consistency, food supply, water turbidity, oxygenation levels, and temperature (Allington-Joneset al., 2010; MacEachernet al., 2012).
Moreover, bioturbation intensity depends on various factors, such as trace maker population densities, types, rates, and depths of trace makers activities, as well as the period over which environmental conditions are favorable for colonization -the colonization window- (Rhoads, 1975; Pollardet al., 1993). When these colonization windows are only briefly open, individual trace fossils are more evident (Savdra, 2009).
The sensitivity of many animals to environmental conditions means that the trace fossils associations can be correspondingly more sensitive environmental indicators than inorganic sedimentary structures (Crimes, 1975). According to Allington-Joneset al. (2010), these associations tend to change progressively with depth, creating a basis for relative bathymetry.
The Cárdenas Formation has been studied for more than 100 years and several studies have demonstrated its paleontological significance documenting ammonites (Ifrimet al., 2005), brachiopods (Myers, 1968; Pérez-Martínez, 2010), corals (Navarro-Moctezuma, 2004; Baron-Szaboet al., 2006), crustaceans (Vegaet al., 1995), echinoderms (Myers, 1968; Navarro-Moctezuma, 2004; Marín-Ávila, 2012), bivalves, gastropods (Böse, 1906), ostracods (Causet al., 2002), rudists (Böse, 1906; Schafhauseret al., 2007; Oviedo-García, 2005; Ponset al., 2013), and foraminifers (Barker and Grimsdale, 1937; Carrillo-Bravo, 1971; Aguilaret al., 2002; Causet al., 2002; Omañaet al., 2008, 2012, 2013). Its ichnological record includes traces ofOphiomorpha nodosa,Skolithos linearis,Diplocraterion parallelum, andPalaeophycus tubularis(Palma-Ramírezet al., 2019).
This paper documents for the very first time the trace fossils occurring in the Cárdenas Formation exposed at the Potrero del Carnero locality, southeastern San Luis Potosí, and discusses their paleoenvironmental implications.
2. Geological setting and study area
Initially, the clastic rocks that constitute the Cárdenas Formation were first described by Böse (1906) in the surroundings of the city of Cárdenas, San Luis Potosí State, with the name of “División Cárdenas”. Later, Burckhardt (1930) used the term “Capas Cárdenas” for this sequence, and subsequently, Imlay (1944) elevated it to formation status. Myers (1968) divided this unit into three informal members (lower, middle, and upper) and proposed three biostratigraphic units based on its invertebrate body fossil assemblages (Durania ojanchalensis,Arcostrea aguilerae, andTampsia floriformisZones). Subsequent work by Carrillo-Bravo (1971) proposed four members (Member 1, Member 2, Member 3, and Member 4) according to the lithological features of this unit. The Cárdenas Formation is a 1,050 m thick unit, deposited during the Upper Cretaceous in a shallow marine setting characterized by fine siliciclastic rocks with interbedded limestone during a transgressive event, cropping out in an asymmetric syncline of the folded Sierra Madre Oriental (Myers, 1968; Carrillo-Bravo, 1971; López-Ramos, 1980).
This unit overlies the El Abra and Tamasopo formations (Myers, 1968; Santamaría-Orozcoet al., 1990; Omañaet al., 2012), and it is unconformably overlain by the Tabaco Formation (Myers, 1968; López-Ramos, 1980; Schafhauseret al., 2007). In accordance with its stratigraphic relations and fossil content, the unit is Campanian-Maastrichtian in age (Carrillo-Bravo, 1971; Schafhauseret al., 2007; Omañaet al., 2012).
The study area is located in the Valles-San Luis Potosí Platform (VSLPP), a Mesozoic paleogeographic positive element where diverse evaporitic and marine Jurassic units, as well as shallow and reef Cretaceous carbonates, were deposited (Carrillo-Bravo, 1971). All these units underlay sandy and argillaceous with calcareous influence sediments (Carrillo-Bravo, 1971; Maldonado-Sarabia and Ríos-Vázquez, 2020). At Potrero del Carnero, Rayón municipality, southwestern San Luis Potosí State, the Cárdenas Formation conformably overlies the Tamasopo Formation (Figure 1; 21°52’18.84 N, 99°26’49.19 W).
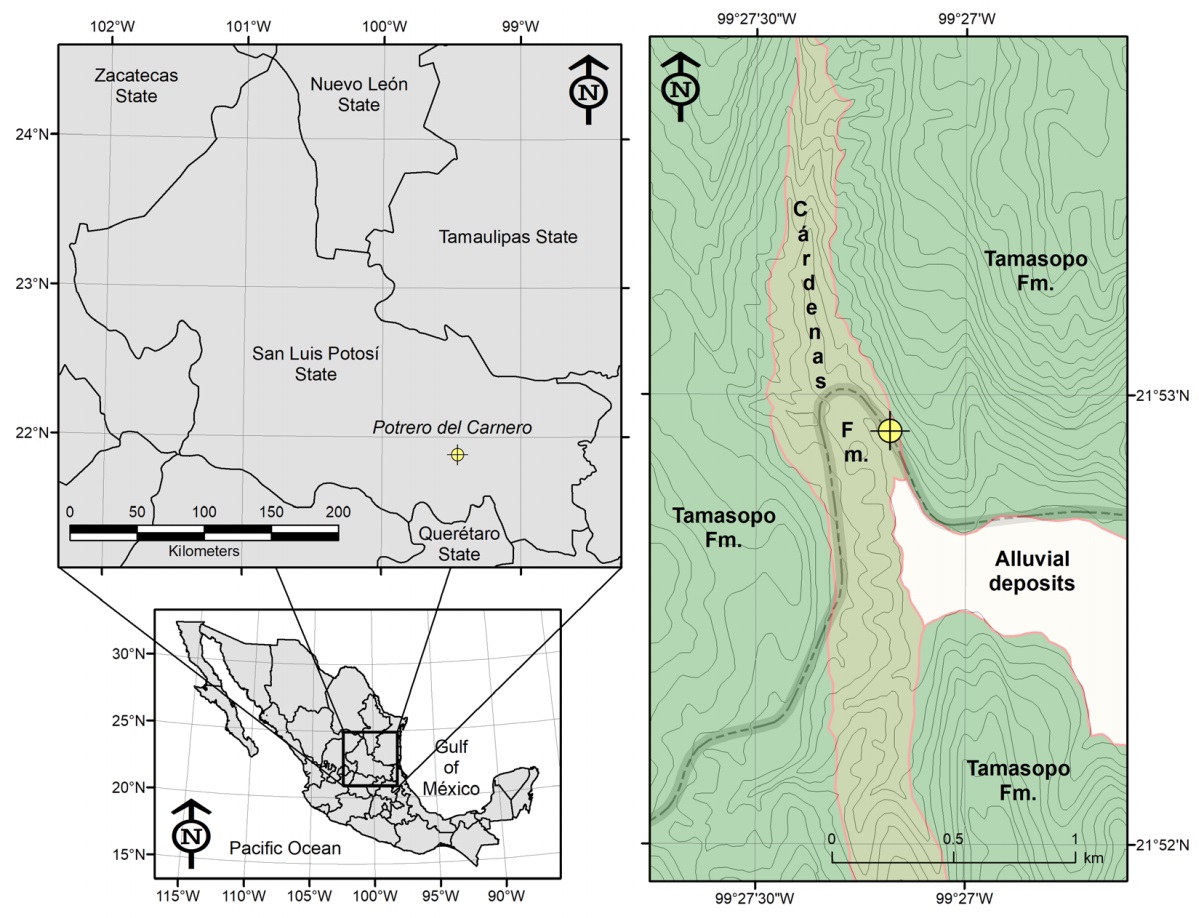
Figure 1 Geographical location and geological map of the studied area. Modified from Maldonado-Sarabia and Ríos-Vázquez (2020).
The only exposed outcrop is composed of a 13 m thick package which begins with limestone horizons of 0.50 to 1.10 m thick, light-brown on weathered surface and grey on fresh surface, with rudists, gastropods, and bivalve impressions. Also, there are sporadic thin horizons (around 0.1 m in thickness) of light-brown siltstone on fresh surfaces. Toward the top of the section, it consists of approximately 2.5 m of sandstone, gray in color on fresh surfaces and ocher on weathered surfaces, intercalated with gray lutite beds. Beds of sandstones range in thickness from 0.18 m to 0.55 m. The lutite is similar to the sandstones in color, with beds being 0.15 m to 0.36 m in thickness.
The trace fossils studied here come from the last 2.5 m of the section and are preserved in the sandstone and lutite beds. In the calcareous levels stratigraphically below the beds bearing the ichnofossils (Figure 2), Flores-Cadenaset al., (2018) recognized the benthic foraminiferaPraechubbina,Chubbina, Cuneolina, as well as miliolids, and nezzazatids from the Campanian-Maastrichtian. However, the presence of the echinodermHemiasterand the ostreidExogyra costataallow to correlate the ichnofossiliferous beds at Potrero del Carnero with theArcostrea aguileraebiozone, in the middle portion of the Cárdenas Formation (early Maastrichtian) (Sohl and Kauffman, 1964; Myers, 1965, 1968; Vegaet al., 1995).
3. Methodology
The trace fossils come from a unique stratigraphic section measured and sampled at Potrero del Carnero locality (Figure 2). Since bed-by-bed sampling was not the main aim of the primary field survey, only a gross stratigraphic assignment is provided. Ichnofossils referred to and figured in this paper were photographed in the field and were not collected. In order to identify the ichnospecies we used the works published by Hadelman (1840), Billings (1862), Ehrenberg (1944), Buatois and Mángano (2011), and Fernández and Pazos (2012). Sedimentary structures, trace fossils, invertebrate fossils, and the intensity of bioturbation were considered for interpretation of the environment of deposition. We follow the scheme proposed by Taylor and Goldring (1993) to indicate the bioturbation intensity of the beds.
Bioturbation index (BI) refers to the determination of the extent of bioturbation or the degree to which the original physical sedimentary structures have been disrupted by biogenic reworking (Droser and Bottjer, 1989; Taylor and Goldring, 1993).
BI categorizes the extent of bioturbation into seven classes: BI=0, no bioturbation (0%); BI=1, sparse bioturbation with few discrete traces (1-4%); BI=2, low bioturbation in sediment that still has preserved sedimentary structures (5-30%); BI=3, moderate bioturbation and still distinguishable bedding boundaries (31-60%); BI=4, intense bioturbation, high trace-fossil density, common overlap of trace fossils, and primary sedimentary structures are mostly erased (61-90%); BI=5, sediment completely disturbed bedding and intense bioturbation (91-99%); BI=6, completely bioturbated and reworked sediment (100%).
4. Systematic ichnology
IchnogenusPlanolites Nicholson, 1873
Planolites beverleyensis Billings, 1862
Description: Traces preserved as positive epirelief, straight to slightly curved, unbranched cylindrical burrows, horizontal to bedding planes. Burrows have smooth surface walls, are 0.8-2.3 cm diameter and up to 30 cm long. The passive fill in the burrow is constituted by gray lutite and the wall lining is not observed (Figures 3C to 3F).
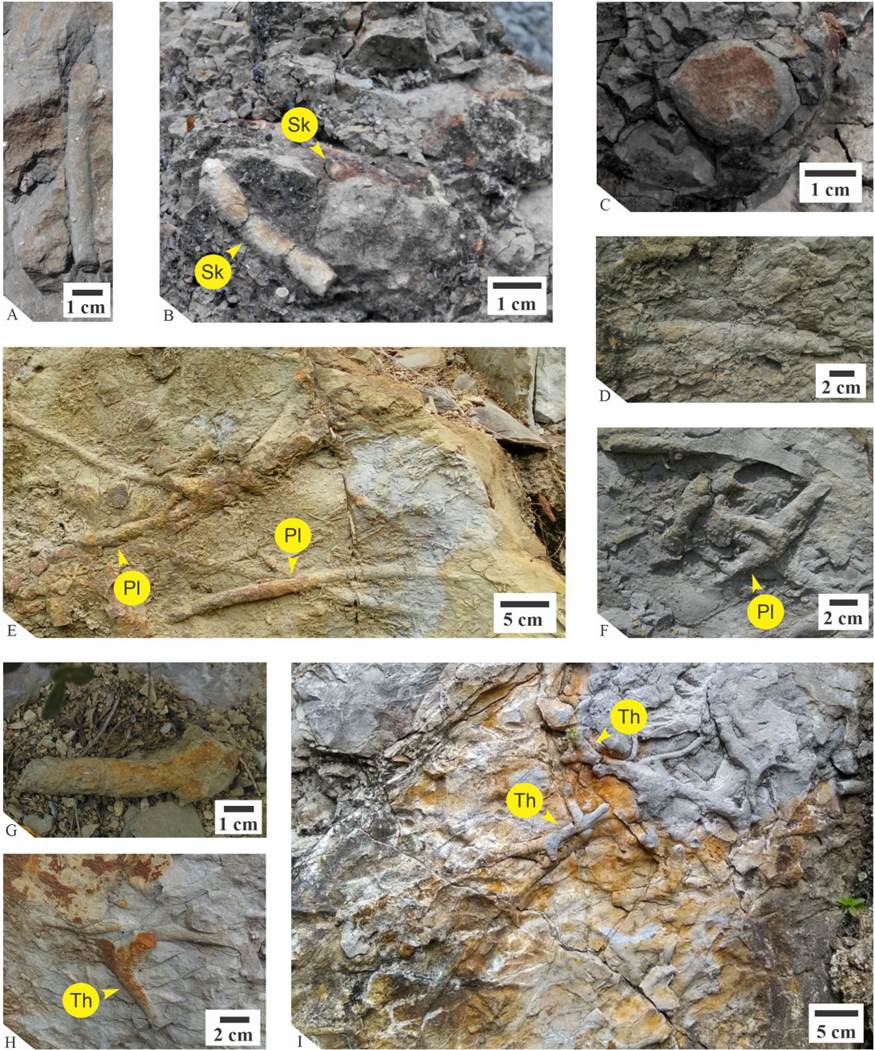
Figure 3 Trace fossils of the Cárdenas Formation in Potrero del Carnero locality. A-B,Skolithos linearis; C, cross-section ofPlanolites beverleyensis; D-F, positive epirelief ofPlanolites beverleyensis; G-H,Thalassinoidesisp.; I, positive epirelief ofP. beverleyensisandThalassinoidesisp
Remarks: Planolitesis ethologically interpreted as pascichnia of deposit feeders (Alpert, 1975; Fürsich, 1998; Knaust, 2010) produced by worms, insects, arthropods, mollusks, or infaunal holothuroids (Bromley, 1996; Uchman, 1998; Buatois and Mángano, 2002; Chenet al., 2011).Planolitesis distinguished fromPalaeophycusby the presence of wall linings and by a burrow-fill identical to the host rock (Pemberton and Frey, 1982; Mánganoet al., 2005).Planolites beverleyensiscan be separated from P.montanusby a minor diameter (P.montanusrarely exceeds 5 mm in diameter while P.beverleyensisrarely is less than 8 mm in diameter) and a markedly more sinuous and undulose of the latter (Pemberton and Frey, 1982).
IchnogenusSkolithos Haldeman, 1840
Skolithos linearis Hadelman, 1840
Description: Straight, vertical to inclined, unbranched cylindrical burrows, with smooth walls. The burrow fill is homogeneous, structureless, medium to fine-grained sandstone, and is similar in composition to the host rock. Burrows are from 0.58 cm to 0.78 cm in width and have a maximum length of 6.238 cm; however, total length is difficult to determine because most specimens pass across the beds (Figure 3A and 3B).
Remarks: Skolithos is documented in a broad variety of environments but is most typical of shallow-water, high-energy settings (Pervesleret al., 2011). It is interpreted as dwelling (domichnia) and feeding (fodinichnia) burrows of annelids, sipunculids, phoronids and polychaete worms, crustaceans, anemones, and probably insects and spiders (Alpert, 1974; Bromley, 1996; Schrlif and Uchman, 2005). From a total of 35 recognized species ofSkolithos, Alpert (1974) validated only five: S.verticalis(Hall), S.linearisHaldeman, S.magnusHowell, S.ingensHowell, and S.annulatusHowell. The main difference between S.verticaliswith S.linearisand S.magnusis the greater diameter in the latter two cases (3-7 mm and 6-12 mm, respectively) (Alpert, 1974; Fernández and Pazos, 2012). On the other hand, S.ingensand S.annulatus, possess a greater diameter and exhibit characteristically ornamented walls (protuberances in S.ingensand annulation in S.annulatus), which are absent in S.verticalis(Fernández and Pazos, 2012).
IchnogenusThalassinoides Ehrenberg, 1944
Thalassinoidesisp. Reit, 1932
Description: Horizontal, branched, cylindrical burrow system with dichotomous bifurcations, from 4 cm to 11 cm in length. Burrows have smooth surface walls, bifurcate in Y or T form with their diameters increasing at bifurcation points, giving the appearance of bulbs or irregular inflations. The tubular wall lining is not observed (Figure 3G to 3I).
Remarks: Thalassinoidesburrows are considered as fodichnial, domichnial, and agrichnial structures (Bromley and Ekdale, 1984; Bromley, 1996; Miller, 2001; Ekdale and Bromley, 2003), attributed to decapod crustaceans, probably thalassinid shrimps or shrimp-like organism, crabs, sea anemones, and acorn worms (Bromley, 1996; Kimet al., 2002; Ekdale and Bromley, 2003; Pervesler and Uchmann, 2009; Chenet al., 2011, 2012). In accordance with Föllmi and Grimm (1990), the crustaceans producingThalassinoidesmay survive transport in turbidity currents and build burrows under anoxic conditions during a limited number of days. Some of the features associated withThalassinoidesare shared with other burrows made by crustaceans namelyOpiomorphaandSpongeliomorpha(Myrow, 1995). However,Thalassinoidescan be distinguished from the others based on the differences among the burrows according to the specific behavioral patterns to specific taxa (Myrow, 1995). In particular,Thalassinoideslacks the pelletal lining ofOphiomorpha(Freyet al., 1978) and the scratchings ofSpongeliomorpha(Bromley, 1967; Frey, 1970).
5. Discussion
The trace fossil record from the Cárdenas Formation at Potrero del Carnero is characterized by burrows belonging toPlanolites beverleyensis, Skolithos linearis, andThalassinoidesisp. The worms and crustaceans are the most probable trace makers of these traces. The aforementioned is congruent with that reported by Vegaet al., (1995), who documented the presence of five decapod families, including two genera of callianassid shrimp. Individual traces are well preserved and are relatively abundant on some beds, which corresponds to BI=3 (moderate) for all bioturbated beds following the proposal of Taylor and Goldring (1993). This grade indicates a moderate level of bioturbation and still distinguishable bedding boundaries (Taylor and Goldring, 1993). The low diversity but high abundance of traces could be explained by stress factors such as oxygen depletion, brackish waters, hypersalinity, high energy, or biological influences such as predation (Taylor and Goldring, 1993; Buatois and Mángano, 2013).
Regarding the traces described herein,Skolithosis mainly recognized in shallow-water environments (Droser and Bottjer, 1989; Fillion and Pickerill 1990; Singhet al., 2008), but also rarely in non-marine settings and deep seas (Neto, 2007; Buatois and Mángano, 2011). This ichnogenus is also typical of the homonymous storm-related ichnofacies (Pemberton and Frey, 1984), and of high-energetic traction sedimentation (Mángano and Buatois, 2004). The ichnospeciesSkolithos linearisis commonly interbedded between the lower offshore and the offshore transition facies, and it records a distinctive onshore-offshore trend (Mánganoet al., 2005). MeanwhilePlanolitesis a eurybathic, extremely facies-crossing ichnogenus (Pemberton and Frey, 1982; Fillion and Pickerill, 1990). In particular,Planolites beverleyensishas been recorded in tempestites (Buatois and Mángano, 2011), as well as in lagoon and offshore bar settings (Tegan, 1992). Finally,Thalassinoidesis a facies-crossing trace fossil, most typical of shallow-marine environment (Freyet al., 1978), associated with both firm and softgrounds (Myrow, 1995, MacEachernet al., 2007).
At Potrero del Carnero, the occurrence of vertical structures indicates opportunistic colonization events, whereas, the presence of horizontal structures is related to fair weather conditions (Perversler and Uchman, 2004; Benkheddaet al., 2021). On the one hand, the presence ofSkolithos lineariscould indicate a storm-related high-energy environment of the lower to middle shoreface (MacEachernet al., 2012), however, more detailed sedimentological studies are needed to reveal this setting. On the other hand, the presence ofThalassinoidescould be interpreted as a shoreface depositional setting, which is supported by the presence of the ostreidExogyra costatathat finds favorable conditions in low energy environments (Myers, 1965). In addition, the co-occurrence ofThalassinoidesandPlanolites, which are essentially horizontal structures, suggest unconsolidated substrate experiencing relatively moderate to low energy in subtidal conditions (Malarkodiet al., 2009). Furthermore, simple morphologies, such asThalassinoides,Skolithos, andPlanolites, are related to salinity-stressed environments, dominating in brackish-water settings (Gingraset al., 2011).
This ichnological assemblage is dominated by dwelling (domichnia) and feeding (fodichnial) traces attributed to suspension- or deposit-feeding organisms, characteristics of the proximalCruzianaIchnofacies (Fürsich, 1998; Buatoiset al., 2002); which is transitional with theSkolithosIchnofacies, and typical of the lower shoreface (Buatois and Mángano, 2011). Besides, theCruzianaIchnofacies is associated with unconsolidated marine substrates, occurring mainly below fair-weather wave base and above storm weather wave base (Pembertonet al., 2001; Patel and Patel, 2015). Previously, based on an ichnological approach, Palma-Ramírezet al. (2019) document theSkolithosIchnofacies in a section of the Cárdenas Formation located southwest of the studied area in this work. These authors suggest a marginal marine setting under low to high energy for early-late Maastrichtian rocks of the Cárdenas Formation exposed at Amoladeras, Rayón municipality, San Luis Potosí state. Due to theCruzianaIchnofacies represents a deeper environment thanSkolithosIchnofacies, and because the age of the studied section here is older than the reported by the section studied by Palma-Ramírezet al., (2019), it is possible to infer that there was a decrease in the sea level throughout the early Maastrichtian in this area. Those above, agree with the documented transgressive-regressive conditions in the VSLPP, where sediment sources for the Cárdenas Formation were located to the west and northwest. The sediments filled an elongated shallow basin that was bordered to the east by a barrier that represented the beginning of folding and uplift of the Sierra Madre Oriental during the initial Laramide pulsations (Vegaet al., 1995).
6. Conclusions
The ichnological study of the Cárdenas Formation at Potrero del Carnero revealed a low ichnodiversity constituted by horizontal and sub-verticall burrows belonging toSkolithos linearis,Planolites beverleyensis, andThalassinoidesisp. Both,Planolites beverleyensisandThalassinoidesisp. represent the first record of these ichnospecies for this lithological unit. This ichnoassemblage corresponds to the proximalCruzianaIchnofacies, suggesting moderate- to low-energy conditions in which food particles tend to accumulate on the sea floor rather than being kept in, with episodic storms.











 nueva página del texto (beta)
nueva página del texto (beta)



