Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Accesos
Accesos
Links relacionados
-
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Revista internacional de contaminación ambiental
versión impresa ISSN 0188-4999
Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient vol.29 no.1 Ciudad de México feb. 2013
Artículos
Mexico City's municipal solid waste characteristics and composition analysis
Características y análisis de composición de los residuos sólidos de la Ciudad de México
Alfonso DURÁN MORENO*, Manuel GARCÉS RODRÍGUEZ, Adriana Rocío VELASCO, Juan Carlos MARÍN ENRIQUEZ, Rafaela GUTIÉRREZ LARA, Abril MORENO GUTIÉRREZ and Norma Angélica DELGADILLO HERNÁNDEZ
Facultad de Química, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. *Autor responsable: alfdur@servidor.unam.mx
Recibido septiembre 2011,
Aceptado noviembre 2012
ABSTRACT
Mexico City generates approximately 12 500 000 kg of municipal solid wastes (MSW) a day. Nowadays, waste management of the refuse material is of high concern since the local landfill has reached its limit capacity and its closure is imminent, thereby alternative disposal methods must be evaluated. The objective of this paper is to analyze the composition of MSW produced in Mexico City through a sampling campaign. In comparison to previous official reports of Mexico City's MSW characterization, in this study the physical composition analysis has been updated and additionally, chemical and physicochemical analysis are included, such as ultimate composition, energy content and heavy metals content.
Key words: Energy content, composition, volumetric weight, ultimate analysis.
RESUMEN
La Ciudad de México genera diariamente alrededor de 12 500 000 kg de residuos sólidos urbanos (RSU). Actualmente, el manejo de este material de rechazo es de gran preocupación debido a que el relleno sanitario Bordo Poniente ha alcanzado su capacidad límite y su cierre es inminente, así que se deben evaluar métodos de disposición alternativos. El objetivo de este documento es analizar la composición de los RSU de la Ciudad de México a través de una campaña de muestreo. En comparación con otros estudios oficiales previos acerca de la caracterización de los RSU de la Ciudad de México, en este estudio la composición física de los RSU es actual y adicionalmente se incluyen análisis químicos y fisicoquímicos, tales como la composición última, el contenido de energía y el contenido de metales pesados.
Palabras clave: contenido de energía, composición, peso volumétrico, análisis último.
INTRODUCTION
Mexico City is the most populated city (INEGI 2005) in the country, about 97 % of its municipal solid wastes (MSW) is disposed in the local landfill "Bordo Poniente" (GDF 2008), which has reached its limit capacity since 2008 (DGSU 2009).
There are not available areas to construct a new landfill in Mexico City or its surroundings. In fact, the Mexico City's government has interest in eliminating the use of landfills and implementing new facilities to separate, to treat and to dispose with energy recovery (GDF 2010).
Studies of characterization of MSW in Mexico City, date to 1999 by the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA 1999) and the latest to 2009, coordinated by the Mexico City's Science and Technology Institute (GDF 2010). Both analyses did not consider detailed information about element composition or energy content.
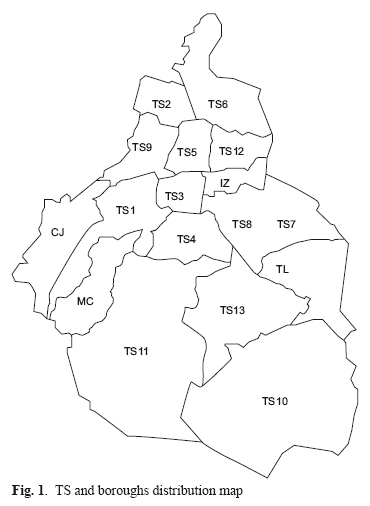
In this work, the MSW samples were collected from the 13 Transfer Stations (TS) located in Mexico City as it is shown in figure 1. The sampling campaign was conducted from November to December, 2009. The analyses were made on homogeneous samples from each transfer unit facility, raised in a period of 3 weeks. Volumetric weight and composition were analyzed in situ, while other determinations such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, ashes, heavy metals content and calorific value were measured in laboratory.
BACKGROUND
Overview of the study area
Mexico City is divided into 16 boroughs named as follows: Álvaro Obregón, Azcapotzalco, Benito Juárez, Coyoacán, Cuajimalpa, Cuauhtémoc, Gustavo A. Madero, Iztacalco, Iztapalapa, Magdalena Contreras, Miguel Hidalgo, Milpa Alta, Tláhuac, Tlalpan, Venustiano Carranza and Xochimilco. Mexico City is the second most populated city in Latin America with an estimated of 8 841 916 habitants in 2009 (CONAPO 2009). The per capita daily generation of MSW is 1.45 kg, higher than the national average (0.98 kg).
MSW management in Mexico City starts with collection by vehicles with a loading capacity between 3000-5000 kg. Next stage is transportation to one of the 13 TS located on 12 of the 16 boroughs in the city (see Fig. 1). Finally waste material is shipped to vehicles with larger capacities to either the composting plant, at the local landfill "Bordo Poniente" or to material recovery facilities. The names and codes of reference to each TS are shown below on table I, along with a data resume of the sampling stage. Waste generated on the boroughs without TS are processed in other facilities. MSW generated in Cuajimalpa borough (CJ) are handled at the TS1, MSW from Iztacalco (IZ) at the TS8, MSW from Magdalena Contreras (MC) at the TS1 and TS11, and MSW generated in Tlahuac (TL) at the TS13.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Size and frequency estimations for samples
Sample size was estimated based on the ASTM D5231 92 (2008) (Standard Test Method for the Determination of the Composition of Unprocessed Municipal Solid Waste). Sample size relies on the component in highest proportion, the desired reliability and other statistical parameters. It resulted on a size of15 samples to obtain representativeness from each TS with an accuracy of 90 %. The 15 samples were raised in one day in each TS, from different collecting vehicles, each sample weighted less than 50 kg and finally a compose sample was formed (500 kg). The sampling method was random selection; the sampling characteristics are in table I.
Sampling procedure
The working area was selected based on the TS operating conditions, therein samples were homogenized. MSW was handled from the discharge area or from collecting vehicles and carried to the working area in a 0.2 m3 container. A 150 kg capacity floor scale was used to measure each MSW sample. A total average weight of the composed sample was 500 kg.
Procedure for homogeneous sample preparation
The procedure was performed with the objective of accurately representing the entire material. The methodology followed the Mexican Standard Test Method "NMX-AA-015-1985" (SECOFI 1985c), which suggests dividing the total sample into four portions and discarding two portions, then repeating the procedure until a significant weight sample is obtained (~ 50 kg). This method and additional procedures of shredding and grinding assure the representativeness of the samples.
Determinations for physical composition
Physical composition measurements were performed in situ according to Mexican Standard Test Method "NMX-AA-022-1985"(SECOFI 1985b). Sub-product classification was based on this technical standard and it was modified with additional categories. Sample weight was measured at each TS by a 150 kg capacity floor scale. The subproducts were weighted on a 20 kg beam balance (0.1 g sensitivity).
Volumetric weight
Volumetric weight was evaluated in situ according to Mexican Standard Test Method "NMX-AA-019-1985" (SECOFI 1985a). Few modifications were applied to the procedure performance: a proportional fraction of material was subtracted from each portion until a 0.1 m3 container was filled. A 150 kg floor scale was used.
Moisture content
Moisture content measurements were carried out under the Mexican Standard Test Method "NMX-AA-016-1984" (SECOFI 1984a) which specifies that each sample most be homogeneous and with a particle size of 5 centimetres. Between 15 to 30 g of sample were placed in an oven at 403 K until the weight was constant. An analytical weight balance with 0.001 g sensitivity and a laboratory oven were used. The oven maintains a constant temperature at 423 K (± 5 K, 1.5 K sensitivity).
Ultimate analysis
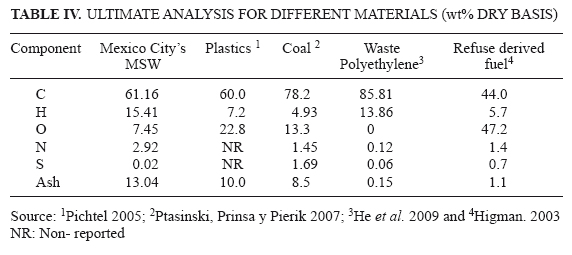
The ultimate analysis of MSW involves determination of mass percentage of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), sulphur (S) and ash and a FISON EA/NA1110 element analyzer was employed. The device measurements are based in sample burning at 1273 K in an oxygen atmosphere. Mass percent is given from composition of flue gases. Mexican Standard Test Method "NMX-AA-018-1984" (SECOFI 1984b) was followed to measure ash content with modifications to avoid fire through the procedure. Dried samples between 1.5 to 4 g were put into a muffle for 1 h at 1073 K. The cooled samples were weighted. A balance (0.1 g sensitivity) and a muffle able to maintain a constant temperature of 1073 K (± 10 K) were used.
Heavy metals detection
Heavy metals quantification was conducted following EPA Method 3051 (USEPA 2007). The samples were prepared by an acid digestion process. This stage was followed by microwave digestion, on a Milestone microwave model 1200 mega. The samples were diluted to detect the metals. Finally, separate detection of each metal was carried out by specific wavelength using a spectrophotometer; the process was performed in a atomic absorption spectrometer (AAnalyst 700, Perkin Elmer).
For Cu, Zn and Mn determination, the flame technique was employed, consisting in an air-acetylene gas mixture, a burner, an electrodeless discharge lamp (EDL) and HNO3 as solvent. For Pb and Cd determination, by a graphite furnace, argon gas and hallow cathode lamps (HCL) were employed. To quantify Hg, the hydride in cold and hot technique was used, and for As, a flow injection system for atomic spectroscopy (FIAS) was used, both techniques utilized a borohydride solution for hydride generation.
Energy content
To estimate the energy released during a combustion process for each sample, a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC, Model 1) Mettler Toledo® was employed. The samples from each TS were homogenized and grinded to dust. In this experiment 3 to 5 mg samples (wt % dry basis) were placed on a 40 (iL aluminium containers, and then heated from 303 K to 773 K at a constant heat rate (3 KJ/min) and a constant oxygen flow. As a result, a thermograph was obtained, where power versus temperature is plotted. The heating value is calculated by heat curve integration. This DSC-1 has a low deviation of reproducibility (<5 %) if it is compared to a pump calorimeter which is higher than 15 %. It guarantees both a full combustion and a temperature measurement from start to end of the process (Mettler Toledo 2010). This equipment has been used to characterize MSW or MSW thermal reactions (Paul et al. 2011 and Rundong et al. 2007).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Hereby results for samples composition are reported for each transfer unit and also a weighted average based on the quantity of waste transferred in each station (See Table A.1).
Physical composition
As a result, the main composition obtained for the MSW generated in Mexico City is shown in table II; the detailed composition is in the Appendix, table A.I.

Almost half of the waste materials generated in Mexico City are organic (49.5 %); a portion of them can be treated by biological technologies to produce biogas or by composting. About 13.16 % are plastics with 6.46 % low density polyethylene bags as main component; 5.7 % is paper and 4 % cardboard. Such materials also have recycling potential, along with glass (2.65 %), ferrous metals (1.16 %), and non-ferrous metals (0.13 %). An important amount of sanitary wastes is found (10.77 %). There are hazardous and special wastes in a low proportion that must be removed from the MSW flow.
Ultimate analysis
Results of ultimate analysis are show in table III. The main component in the samples was carbon in a range from 50.4 % (TS4) to 75.5 % (TS3). The component with the lowest occurrence was sulphur, which was detected only in TS7 with 0.2 % (wt % dry basis). Weighted average indicates that chemical composition for the Mexico City's MSW is: C- 61.2 %, H-15.4 %, N-2.92 %, S-0.02 %, O-7.45 % and Ash-13.0 %; resulting on a formula for the volatile fraction as follows:
C7,125H22,066O938N309S
The weighted average content of carbon (61.2 wt % dry basis) is similar to plastics carbon content (wt % dry basis) (Pichtel 2005).
The Mexico City's MSW ash content value is in the typical range of 10-20 % for wastes (Tchobanoglous 2002).
Physical characteristics
Moisture, organic fraction and ashes content, as well as volumetric weight from Mexico City's MSW are presented in table V. The organic fraction of MSW contributes with the highest amount of moisture, as it can be seen in other characterization studies that report values around 65 % of moisture content for the organic fraction (Menkipura et al. 2008 and Igonia et al. 2007). The organic fraction (49.5 %) in the MSW influences the moisture content (33.7 %).
Volumetric weight is useful in designing management strategies such as transportation; these values depend on the physical composition, moisture content and compaction level. Weighted average for volumetric weight (185.9 kg/m3) is above the common range (150-180 kg/m3) reported for MSW (Pichtel 2005). This difference relies on the influence of organic waste from TS Iztapalapa. It contributes 24 % to the total amount of MSW handled in transfer stations and a high volumetric weight of 288.0 kg/m3. The organic waste contained in this stream is high because its source is the main suppling center of fruits and vegetables in the city. The values obtained were in a range from 145.7 to 288.0 kg/m3.
High heating value
Many variables, such as moisture affect the energy content, Mexico City's MSW average high heating value (HHV) is of 10.9 MJ/kg. Values for each TS are in table V. The low heating value (LHV) has been calculated according to equation (1) Pichtel (2005):
LHV = HHV [MJ/kg] - 0.0244(M + 9H) (1)
For equation (1) moisture (M) and hydrogen (H) variables represent the percentages of water, and hydrogen on dry basis, respectively. The LHV for the moisture and hydrogen content determined in this research (33.7 %, and 15.4 %, respectively) is 6.7 MJ/kg.
Heavy metals content
Regarding heavy metals, they are present in small amounts in Mexico City's MSW as shown in table VI. These elements are present as a result of batteries, consumer electronics, ceramics, light bulbs and paint chips, among others. The metals As, Cu, Cr, Hg, Pb, Zn and Mn are harmful to human and animal health at certain concentrations and therefore should receive close monitoring. For instance, in MSW thermal treatment, heavy metals are monitored in ashes (Shi et al. 2008).

Comparing values for heavy metals content in ashes from an incineration process in China reported by Shi et al. (2008) it can be stated that values for As, Cu (except TS8 sample), Cr, Mn (except TS8 sample), Pb and Zn contents are below values reported in any stage of the process measurements (fly ash from boiler, bottom ash and fly ash from bag filter).
CONCLUSIONS
Characterization was realized for samples collected from a campaign considering the 13 TS located in Mexico City. Average values are weighted, according to the quantity of MSW transferred in each station. The organic fraction is the most abundant (49.5 %). The recyclable material composed by cardboard, paper and plastics has an average value of 24 %. The general formula for Mexico City's MSW resulted onC7,125H22,066O938N309S, (wt % dry basis), average content of moisture of 33.7 % and an ash content of 13 %. The MSW management includes several strategies such as minimization in source, recycling, reuse, thermal treatment, final disposition among others. Results of this study can be considered to evaluate strategies. The energy content (HHV) obtained for Mexico City' MSW is 10.9 MJ/kg. This value is expected to increase in the near future as soon as the separated collection is achieved.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Mexico City Government and the Mexican Science and Technology National Council (CONACyT) through the project CONACyT-GDF DF-2008-C01-94261.
Special thanks to our staff: N. Cabrera Delgado, J. T. Espinoza Sandoval , I. E. García Lizalde, S. Mayorga Castillo, S. Palacios González, J. J. Rodríguez Escobar and L. Romano Pardo for their technical support for the MSW sampling campaign; and to Ph. D. E. Rincon A. for providing assistance.
REFERENCES
ASTM (2008). ASTM D5231 92 Standard Test Method for Determination of the Composition of Unprocessed Municipal Solid Wastes. American Society for Testing and Materials. [ Links ]
Castells X. (2005). Tratamiento y valorización energética de residuos. Ediciones Díaz de Santos, España, 1228 pp. [ Links ]
CONAPO (2009). Población a mitad de año según tamaño de la localidad por Entidad Federativa, 2005-2030 (en línea). Consejo Nacional de Población, México. www.conapo.gob.mx/00cifras/proy/localidad.xl 16/03/10. [ Links ]
DGSU (2009). Recolección, Transferencia, Selección y Disposición Final (en línea). Dirección General de Servicios Urbanos, Gobierno del Distrito Federal, México. http://www.obras.df.gob.mx/?page_id=85 01/07/10. [ Links ]
GDF (2008). Inventario de Residuos Sólidos Urbanos del Distrito Federal. Secretaría del Medio Ambiente del Gobierno del Distrito Federal. Inventario. Ciudad de México, 49 pp. [ Links ]
GDF (2010). Programa de Manejo Integral de Residuos Sólidos del Distrito Federal. Gobierno del Distrito Federal. Programa. Ciudad de México, 69 pp. [ Links ]
Göransson K., Sõderlind U., He J. and Zhang W. (2011). Review of syngas production via biomass DFBGs. Renew. Sus. Energ. Rev. 15, 482-492. [ Links ]
He M., Xiao B., Hu Z., Liu S., Guo X. and Luo S. (2009). Syngas production from catalytic gasification next term of waste polyethylene: Influence of temperature on gas yield and composition. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 34, 1342-1348. [ Links ]
Highman C. (2003). Gasification. Elsevier Science, USA, 391 pp. [ Links ]
Igonia A.H., Ayotamunoa M.J., Ogajib S.O.T. and Probertb S.D. (2007). Municipal solid-waste in Port Harcourt. Nigeria. Appl. Ener. 84, 664-670. [ Links ]
INEGI (2005). II Count of Population and Housing (en línea). http://www.inegi.gob.mx/est/contenidos/espanol/rutinas/ept.asp?t=mpob93&c=3839&e=08 01/07/11. [ Links ]
JICA (1999). Solid Waste Management Study for Mexico City. Japan International Cooperation Agency, Technical Report, Mexico City,131 pp. [ Links ]
Menkipura S.M.N. and Basnayake B.F.A. (2008). New applications of 'Hess Law' and comparisons with models for determining calorific values of municipal solid wastes in the Sri Lankan context. Renewable Energ. 34, 1587-1594. [ Links ]
Mettler Toledo (2010). Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Technical Report, Switzerland, 14 pp. [ Links ]
Paul J., Tretsiakova-McNally S. and Mckenna S (2011). Characterization of cellulosic wastes and gasification products from chicken farms. Waste Manage. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2011.09.024 [ Links ]
Pichtel J. (2005). Waste Management Practices: Municipal, hazardous and industrial. Taylor & Francis. Florida, USA. 659 pp. [ Links ]
Ptasinski K. J., Prinsa M. J. and Pierik A. (2007). Exergetic evaluation of biomass gasification. Energy 32, 568-574. [ Links ]
Rundong L., Wang L., Yang T. and Bernhard R.(2007). Investigation of MSW fly ash melting characteristic by DSC-DTA. Waste Manage. 27, 1383-1392. [ Links ]
SECOFI (1984a). Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-016-1984. Protección al ambiente - Contaminación del Suelo -Residuos Sólidos Municipales - Determinación de Humedad. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. 10 de diciembre de 1984. [ Links ]
SECOFI (1984b). Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-018-1984. Protección al ambiente - contaminación de suelo -Residuos Sólidos Municipales - Determinación de Cenizas. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. 10 de diciembre de 1984. [ Links ]
SECOFI (1985a). Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-019-1985. Protección al Ambiente -Contaminación del Suelo -Residuos Sólidos Municipales - Peso Volumétrico "In Situ". Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Diario Oficial de la Federación. 18 de marzo de 1985. [ Links ]
SECOFI (1985b). Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-022-1985. Protección al Ambiente - Contaminación al suelo - -Residuos Sólidos Municipales - Selección y Cuantificación de Subproducos. Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Diario Oficial de la Federación. 18 de marzo de 1985. [ Links ]
SECOFI (1985c). Norma Mexicana NMX-AA-015-1985. Protección al Ambiente Contaminación del suelo -Residuos Sólidos Municipales - Muestreo - Método de Cuarteo - Secretaría de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Diario Oficial de La Federación.15 de agosto de 2003. [ Links ]
Shi D., Wu W., Lu S., Chen T., Huang H., Chen Y. and Yan J. (2008). Effect of MSW source-classified collection on the emission of PCDDs/Fs and heavy metals from incineration in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 153, 685-694. [ Links ]
Tchobanoglous G. (2002). Handbook of solid waste management. McGraw- Hill. New York, USA. 950 pp. [ Links ]
USEPA (2007). Method 3051. Microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils and oils.United States Environmental Protection Agency. USA. 30 pp. [ Links ]
World Bank (2008). Technical presentation "Municipal Solid Waste Treatment Technologies and Carbon Finance". Carbon Finance Unit. [ Links ]














