Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO -
 Access statistics
Access statistics
Related links
-
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO
Share
Revista mexicana de astronomía y astrofísica
Print version ISSN 0185-1101
Rev. mex. astron. astrofis vol.47 n.1 Ciudad de México Apr. 2011
Mass and metal ejection efficiency in disk galaxies driven by young stellar clusters of nuclear starburst
A. Rodríguez–González,1 A. Esquivel,1 A. C. Raga,1 and P. Colín2
1 Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares. Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Apdo. Postal 70–543, 04510 México, D. F., México (esquivel@nucleares.unam.mx, raga@nucleares.unam.mx, ary@nucleares.unam.mx).
2 Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Apdo. Postal 3–72, 58090 Morelia, Michoacán, México (p.colin@crya.unam.mx).
Received 2010 August 26
Accepted 2011 January 31
RESUMEN
Presentamos las eficiencias de pérdida de masa y metales obtenidas de modelos numéricos de vientos galácticos empujados por la energía depositada en brotes de formación estelar nucleares. Los brotes de formación estelar contienen cúmulos estelares jóvenes los cuales inyectan la energía suficiente para empujar parte del medio interestelar fuera de las galaxias. En algunos casos los vientos galácticos contienen una importante parte de los metales producidos por las nuevas generaciones estelares. Para estudiar las eficiencias de pérdida de masa y metales hemos desarrollado simulaciones numéricas 3D N– Cuerpos/Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics de vientos galácticos para los casos: adiabáticos y con pérdidas radiativas. Los modelos numéricos cubren una amplio intervalo de masas de los brotes de formación estelar 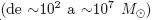 y de masas en las galaxias anfitrionas
y de masas en las galaxias anfitrionas 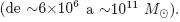 Las regiones de formación estelar concentradas en el centro del potencial son una maquinaria importante para la pérdida y redistribución de masa y metales en este tipo de galaxias.
Las regiones de formación estelar concentradas en el centro del potencial son una maquinaria importante para la pérdida y redistribución de masa y metales en este tipo de galaxias.
ABSTRACT
We present results from models of galactic winds driven by energy injected by nuclear starbursts. The total energy of the starburst is provided by young central stellar clusters and parts of the galactic interstellar médium are pushed out as part of the galactic wind (in some cases the galactic wind contains an important part of the metáis produced in the new generation of stars). We have performed adiabatic and radiative 3D N–Body/Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics simulations of galactic winds using the GADGET–2 code. The numerical models cover a wide range of starburst 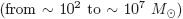 and galactic gas masses
and galactic gas masses 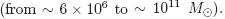 The concentrated central starburst regions are an efficient engine for producing the mass and metal loss in galaxies, and also for driving the metal redistribution in galaxies.
The concentrated central starburst regions are an efficient engine for producing the mass and metal loss in galaxies, and also for driving the metal redistribution in galaxies.
Key Words: galaxies: starburst — galaxies: star clusters: general — ISM: general — stars: winds, outflows.
DESCARGAR ARTÍCULO EN FORMATO PDF
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank the anonymous referee for very relevant comments that resulted in a substantial revision of the original version of this paper. We thank Volker Springel (from the Univ. of Heidelberg) for helpful suggestions which we have been included in this paper. We acknowledge support from the Conacyt grants 61547, 101356 and 101975.
REFERENCES
Anders, P., de Grijs, R., Fritze–v. Alvensleben, U., & Bissantz, N. 2004, MNRAS, 347, 17 [ Links ]
Cantó, J., Raga, A. C, & Rodríguez, L. F. 2000, ApJ, 536, 896 [ Links ]
Chevalier, R. A., & Clegg, A. W. 1985, Nature, 317, 44 [ Links ]
Cooper, J. L., Bicknell, G. V., Sutherland, R. S., & Bland–Hawthorn, J. 2008, ApJ, 674, 157 [ Links ]
D'Ercole, A., & Brighenti, F. 1999, MNRAS, 309, 941 [ Links ]
De Young, D. S., & Heckman, T. M. 1994, ApJ, 431, 598 [ Links ]
Fragile, P. C, Murray, S. D., & Lin, D. N. C. 2004, ApJ, 617, 1077 [ Links ]
Fujita, A., MacLow, M.–M., Ferrara, A., & Meiksin, A. 2004, ApJ, 613, 159 [ Links ]
Fujita, A., Martín, C. L., MacLow, M.–M., New, K. C. B., & Weaver, R. 2009, ApJ, 698, 693 [ Links ]
Harris, J., Calzetti, D., Gallagher, J. S., Conselice, C. J., & Smith, D. A. 2001, AJ, 122, 3046 [ Links ]
Heckman, T. M., Armus, L., & Miley, G. K. 1990, ApJS, 74, 833 [ Links ]
Kroupa, P., Tout, C. A., & Gilmore, G. 1993, MNRAS, 262, 545 [ Links ]
Hernquist, L. 1990, ApJ, 356, 359 [ Links ]
––––––––––. 1993, ApJ, 409, 548 [ Links ]
Larson, R. B. 1974, MNRAS, 169, 229 [ Links ]
Leitherer, C, & Heckman, T. M. 1995, ApJS, 96, 9 [ Links ]
Leitherer, C, et al. 1999, ApJS, 123, 3 [ Links ]
Lynds, C. R., & Sandage, A. R. 1963, ApJ, 137, 1005 [ Links ]
MacLow, M. M., & Ferrara, A. 1999, ApJ, 513, 142 [ Links ]
Martín, C. L. 1999, ApJ, 513, 156 [ Links ]
Meló, V. P. 2005, PhD Thesis, Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Spain [ Links ]
Meló, V. P., Muñoz–Tuñón, C, Maíz–Apellániz, J., & Tenorio–Tagle, G. 2005, ApJ, 619, 270 [ Links ]
Meynet, G., & Maeder, A. 2002, A & A, 390, 561 [ Links ]
Moorwood, A. F. M. 1996, Space Sci. Rev., 77, 303 [ Links ]
Navarro, J. F., Frenk, C. S., & White, S. D. M. 1996, ApJ, 462, 563 (NFW) [ Links ]
Ohyama, Y., et al. 2002, PASJ, 54, 891 [ Links ]
Pettini, M., et al. 2001, ApJ, 554, 981 [ Links ]
Pilyugin, L. S. 1993, A & A, 277, 42 [ Links ]
Recchi, S., Matteucci, F., & D'Ercole, A. 2001, MNRAS, 322, 800 [ Links ]
Recchi, S., Matteucci, F., D'Ercole, A., & Tosi, M. 2002, A & A, 384, 799 [ Links ]
Recchi, S., Spitoni, E., Matteucci, F., & Lanfranchi, G. A. 2008, A & A, 489, 555 [ Links ]
Rodríguez–González, A., Raga, A. C, & Cantó, J. 2009, A & A, 501, 411 [ Links ]
Scannapieco, C, Tissera, P. B., White, S. D. M., & Springel, V. 2005, MNRAS, 364, 552 [ Links ]
Shopbell, P. L., & Bland–Hawthorn, J. 1998, ApJ, 493, 129 [ Links ]
Smith, L. J., et al. 2007, ApJ, 667, 145 [ Links ]
Springel, V. 2000, MNRAS, 312, 859 [ Links ]
––––––––––. 2005, MNRAS, 364, 1105 [ Links ]
Springel, V., Di Matteo, T., & Hernquist, L. 2005, 361, 776 [ Links ]
Springel, V., Yoshida, N., & White, S. 2001, New Astron., 6, 79 [ Links ]
Strickland, D., & Stevens, S. 2000, MNRAS, 314, 511 [ Links ]
Sutherland, R. S., & Dopita, M. A. 1993, ApJS, 88, 253 [ Links ]
Tenorio–Tagle, G. 1996, AJ, 111, 1641 [ Links ]
Tenorio–Tagle, G., & Muñoz–Tuñón, C. 1998, MNRAS, 293, 299 [ Links ]
Tenorio–Tagle, G., Silich, S., & Muñoz–Tuñón, C. 2003, ApJ, 597, 279 [ Links ]
Tenorio–Tagle, G., Silich, S., Rodríguez–González, A., & Muñoz–Tuñón, C. 2005, ApJ, 620, 217 [ Links ]
Tomisaka, K., & Ikeuchi, S. 1988, ApJ, 330, 695 [ Links ]
Veilleux, S., Cecil, G., & Bland–Hawthorn, J. 2005, ARA & A, 43, 769 [ Links ]
Westmoquette, M. S., Exter, K. M., Smith, L. J., & Gallagher, J. S. 2007, MNRAS, 381, 894 [ Links ]
Westmoquette, M. S., Smith, L. J., & Gallagher, J. S. 2008, MNRAS, 383, 864 [ Links ]
White, S. D. M., & Frenk, C. S. 1991, MNRAS, 379, 52 [ Links ]
White, S. D. M., & Rees, M. J. 1978, MNRAS, 183, 341 [ Links ]














