Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Acessos
Acessos
Links relacionados
-
 Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO
Compartilhar
Revista mexicana de astronomía y astrofísica
versão impressa ISSN 0185-1101
Rev. mex. astron. astrofis vol.44 no.1 Ciudad de México Jan. 2008
Determination of the IMF in the LMC stellar cluster NGC 2156
E. Silva–Villa,1,2 M. Sirianni,1,3 and J. Zuluaga2
1 Space Telescope Science Institute, 3700 San Martin Drive, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA (E.SilvaVilla@astro.uu.nl, sirianni@stsci.edu).
2 Instituto de Física, Universidad de Antioquia, A. A.1226, Medellín, Colombia (zuluaga@fisica.udea.edu.co).
3 Science Operation Development Division, European Space Agency, The Netherlands.
Received 2007 August 15
Accepted 2007 October 23
RESUMEN
Presentamos un estudio de la IMF del cúmulo estelar NGC 2156 de la LMC usando imágenes tomadas por el telescopio espacial Hubble en las bandas F555W y F814W. El estudio forma parte de un programa dedicado a investigar si la IMF para estrellas de baja masas es dependiente de las condiciones locales, observando cúmulos jóvenes en la LMC y SMC. Hemos detectado estrellas hasta una magnitud límite de m555 = 26, correspondiente a una masa estelar de 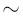 0.6M
0.6M a la distancia de la LMC (50.11 Kpc). La comparación de los diagramas CMD con isocronas teóricas indica una edad de 49 ± 5 Myr para este cúmulo. Se realizó un análisis de completitud y una determinación de la contaminación de estrellas de fondo para corregir la LF y así derivar la MF del cúmulo, usando la relación ML estándar para estrellas de la secuencia principal. Dado que el cúmulo es muy joven, la MF observada es una buena aproximación a la IMF.
a la distancia de la LMC (50.11 Kpc). La comparación de los diagramas CMD con isocronas teóricas indica una edad de 49 ± 5 Myr para este cúmulo. Se realizó un análisis de completitud y una determinación de la contaminación de estrellas de fondo para corregir la LF y así derivar la MF del cúmulo, usando la relación ML estándar para estrellas de la secuencia principal. Dado que el cúmulo es muy joven, la MF observada es una buena aproximación a la IMF.
ABSTRACT
We present a study on the IMF of the stellar cluster NGC 2156 in the LMC from deep HST–WFPC2 images in the bands F555W and F814W. The study is part of a larger program to investigate whether the IMF at low stellar masses is dependent on local conditions by observing young globular clusters in the LMC and the SMC. We detected stars down to a limiting magnitude of m555 = 26, which corresponds to stellar masses of 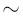 0.6 M
0.6 M at the distance of the LMC (50.11 Kpc). A comparison of the cluster CMD with theoretical isochrones indicates an age of 49 ± 5 Myr. We performed a completeness analysis and determined the background stellar contamination to correct the observed LF and derive the MF of the cluster using the standard ML–relation for main sequence stars. Given the fact that the cluster is very young, the present day MF is expected to be a good approximation to the IMF.
at the distance of the LMC (50.11 Kpc). A comparison of the cluster CMD with theoretical isochrones indicates an age of 49 ± 5 Myr. We performed a completeness analysis and determined the background stellar contamination to correct the observed LF and derive the MF of the cluster using the standard ML–relation for main sequence stars. Given the fact that the cluster is very young, the present day MF is expected to be a good approximation to the IMF.
Key Words: methods: data analysis — stars: formation — stars: low–mass — stars: luminosity function, mass function — techniques: image processing
DESCARGAR ARTÍCULO EN FORMATO PDF
Acknowledgement
Esteban Silva–Villa acknowledges the Space Telescope Scientific Institute (STScI) for its financial support and hospitality during a stay as a Summer Student (2004) and as an invited astronomer (2005) in Baltimore, where the main part of this work was performed. The authors also thank Luz Angela Cubides for proof reading.
REFERENCES
Bica, E. L. D., Schmitt, H. R., Dutra, C. M., & Oliveira, H. L. 1999, AJ, 117, 238 [ Links ]
Claudius, M., & Grosbol, P. J. 1980, A & A, 87, 339 [ Links ]
D'Antona, F. 1998, in ASP Conf. Ser. 142, The Stellar Initial Mass Function, ed. G. Gilmore & D. Howell (San Francisco: ASP), 157 [ Links ]
Dolphin, A. E. 2000, PASP, 112, 1397 [ Links ]
Elson, R. A. W. 1991, Ap J S, 76, 185 [ Links ]
Holtzman, J. A., Burrows, C. J., Casertano, S., Hester, J. J., Trauger, J. T., Watson, A. M., & Worthey, G. 1995, PASP, 107, 1065 [ Links ]
Kalirai, J. S., Fahlman, G. G., Richer, H. B., & Ventura, P. 2003, AJ, 126, 1402 [ Links ]
Kennicutt, R. C., Jr. 1998, in ASP Conf. Ser. 142, The Stellar Initial Mass Function, ed. G. Gilmore & D. Howell (San Francisco: ASP), 1 [ Links ]
Kroupa, P. 2001, MNRAS, 322, 231 [ Links ]
Kroupa, P., & Boily, C. M. 2002, MNRAS, 336, 1188 [ Links ]
Kroupa, P., Tout, C. A., & Gilmore, G. 1990, MNRAS, 244, 76 [ Links ]
_________. 1993, MNRAS, 262, 545 [ Links ]
Lejeune, T., & Schaerer, D. 2001, A & A, 366, 538 [ Links ]
Massey, P. 2003, ARA & A, 41, 15 [ Links ]
Miller, G. E., & Scalo, J. M. 1979, Ap J S, 41, 513 [ Links ]
Nota, A. 1999, HST Proposal 8134, Stellar Populations in Clusters [ Links ]
Phelps, R. L., & Janes, K. A. 1993, AJ, 106, 1870 [ Links ]
Prisinzano, L., Carraro, G., Piotto, G., Seleznev, A. F., Stetson, P. B., & Saviane, I. 2001, A & A, 369, 851 [ Links ]
Prisinzano, L., Micela, G., Sciortino, S., & Favata, F. 2003, A & A, 404, 927 [ Links ]
Salpeter, E. 1955, Ap J, 121, 161 [ Links ]
Sagar, R., Munari, U., & de Boer, K. S. 2001, MNRAS, 327, 23 [ Links ]
Sanner, J., & Geffert, M. 2001, A & A, 370, 87 [ Links ]
Scalo, J. M. 1986, Fundam. Cosmic Phys., 11, 1 [ Links ]
_________. 1998, in ASP Conf. Ser. 142, The Stellar Initial Mass Function, ed. G. Gilmore & D. Howell (San Francisco: ASP), 201 [ Links ]
Sirianni, M., Nota, A., Leitherer, C., De Marchi, G., & Clampin, M. 2000, Ap J, 533, 203 [ Links ]
Smecker–Hane, T. A., Cole, A. A., Gallagher, J. S., III, & Stetson, P. B. 2002, Ap J, 566, 239 [ Links ]
Sung, H., & Bessell, M. S. 2004, AJ, 127, 1014 [ Links ]
Taff, L. G. 1974, AJ, 79, 1280 [ Links ]Tarrab, I. 1982, A & A, 109, 285 [ Links ]
van den Bergh, S. 1957, Ap J, 125, 445 [ Links ]
Yadav, R. K. S., & Sagar, R. 2002, MNRAS, 337, 133 [ Links ]
_________. 2004, MNRAS, 351, 667 [ Links ]














