Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Accesos
Accesos
Links relacionados
-
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Revista mexicana de física
versión impresa ISSN 0035-001X
Rev. mex. fis. vol.54 no.1 México feb. 2008
Investigación
Hydrogen atom in a magnetic field: electromagnetic transitions of the lowest states
J.C. López Vieyra and H.O. Pilón
Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, UNAM, Apartado Postal 70–543, 04510 México, e–mail: vieyra@nucleares.unam.mx, horop@nucleares.unam.mx
Recibido el 29 de septiembre de 2007
Aceptado el 5 de diciembre de 2007
Abstract
A detailed study of the lowest states 1s0, 2p–1, 2p0 of the hydrogen atom placed in a magnetic field B 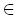 (0 — 4.414 × 1013 G) and their electromagnetic transitions (1s0
(0 — 4.414 × 1013 G) and their electromagnetic transitions (1s0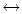 2p–1 and 1s0
2p–1 and 1s0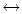 2p0) is carried out in the infinite–proton–mass (Born–Oppenheimer) approximation. The variational method is used with a physically motivated recipe to design simple trial functions applicable to the whole domain of magnetic fields. We show that the proposed functions yield very accurate results for the ionization (binding) energies. Dipole and oscillator strengths are in good agreement with results by Ruder et al. [10], although we observe deviations of up to ~ 30% for the oscillator strength of the linearly polarized electromagnetic transition 1s0
2p0) is carried out in the infinite–proton–mass (Born–Oppenheimer) approximation. The variational method is used with a physically motivated recipe to design simple trial functions applicable to the whole domain of magnetic fields. We show that the proposed functions yield very accurate results for the ionization (binding) energies. Dipole and oscillator strengths are in good agreement with results by Ruder et al. [10], although we observe deviations of up to ~ 30% for the oscillator strength of the linearly polarized electromagnetic transition 1s0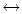 2p0 at strong magnetic fields B
2p0 at strong magnetic fields B 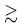 1000 a.u.
1000 a.u.
Keywords: hydrogen atom; magnetic fields; transitions.
Resumen
Se lleva a cabo un estudio detallado de los estados mas bajos 1s0, 2p–1, 2p0del átomo de hidrógeno en un campo magnético B 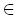 (0 — 4.414 × 1013 G) y sus transiciones electromagnéticas (1s0
(0 — 4.414 × 1013 G) y sus transiciones electromagnéticas (1s0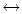 2p–1 and 1s0
2p–1 and 1s0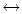 2p0) en la aproximación de masa del protón infinita (Born–Oppeneimer). Se usa el método variacional con una receta físicamente motivada para diseñar funciones de prueba simples aplicables a el rango completo de campos magnéticos. Mostramos que las funciones propuestas arrojan resultados muy precisos para las energías de ionización (energías de amarre). Las fuerzas de dipolo y de oscilador están en buen acuerdo con los resultados de Ruder et al. [10] aunque observamos desviaciones de hasta ~ 30% para la fuerza de oscilador de la transición electromagnética linealmente polarizada 1s0
2p0) en la aproximación de masa del protón infinita (Born–Oppeneimer). Se usa el método variacional con una receta físicamente motivada para diseñar funciones de prueba simples aplicables a el rango completo de campos magnéticos. Mostramos que las funciones propuestas arrojan resultados muy precisos para las energías de ionización (energías de amarre). Las fuerzas de dipolo y de oscilador están en buen acuerdo con los resultados de Ruder et al. [10] aunque observamos desviaciones de hasta ~ 30% para la fuerza de oscilador de la transición electromagnética linealmente polarizada 1s0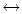 2p0 para campos magnéticos B
2p0 para campos magnéticos B 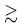 1000 a.u.
1000 a.u.
Descriptores: átomo de hidrógeno; campos magnéticos; transiciones.
PACS: 31.15.Pf; 31.10.+z; 32.60.+i; 97.10.Ld
DESCARGAR ARTÍCULO EN FORMATO PDF
References
1. W. Becker and G. Pavlov, Pulsars and isolated neutron stars, Edited by Johan A.M. Bleeker, Johannes Geiss and Martin C.E. Huber, The century of Space Science Volume 1, Kluwer Academic Publishers, (2001) 721; (astro–ph/208356). [ Links ]
2. V.E. Zavlin, Thermal emission from isolated neutron stars: theoretical and observational aspects (2007); astro–ph/0702426v1. [ Links ]
3. D. Sanwal, G.G. Pavlov, V.E. Zavlin and M.A. Teter, ApJL 574 (2002) L61; (astro–ph/0206195). [ Links ]
4. M.H. van Kerkwijk et al., ApJ 608 (2004) 432; (astro–ph/0311195). [ Links ]
5. A.V. Turbiner and J.–C. Lopez Vieyra, Mod. Phys. Lett. A 19 (2004) 1919; (astro–ph/0404290). [ Links ]
6. A. V. Turbiner, A helium–hydrogenic molecular atmosphere of neutron star 1E1207.4–5209, Contribution to Physics Of Neutron Stars – 2005, June 27 – 29, Ioffe Physico–Technical Institute, Saint–Petersburg, Russia (2005); (astro–ph/0506677). [ Links ]
7. K. Mori and W.C.G. Ho, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 377 (2007) 905; (astro–ph/0611145). [ Links ]
8. K. Mori and J.S. Heyl, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 376 (2007) 895; (astro–ph/0610253v2). [ Links ]
9. R.H. Garstang, Rep. Prog. Phys. 40 (1976) 105. [ Links ]
10. H. Ruder, G. Wunner, H. Herold, and F. Geyer, Atoms in strong magnetic fields (Springer–Verlag, 1994). [ Links ]
11. Yu. P Kravchenko, M.A. Liberman and B. Johansson, Phys. Rev. A 54 (1996) 287. [ Links ]
12. B.M. Karnakov and V.S. Popov, ZhETF 124 (2003) 996; JETP 97 (2003) 890 (English Translation). [ Links ]
13. A.V. Turbiner, ZhETF 79 (1980) 1719; Soviet Phys.–JETP 52 (1980) 868 (English Translation); Usp. Fiz. Nauk. 144 (1984) 35; Sov. Phys. – Uspekhi 27 (1984) 668 (English Translation); Yad Fiz. 46 (1987) 204; Sov. Journ. of Nucl. Phys. 46 (1987) 125 (English Translation); Doctor of Sciences Thesis, ITEP, Moscow, 1989 (unpublished), Analytic Methods in Strong Coupling Regime (large perturbation) in Quantum Mechanics. [ Links ]
14. I.I. Sobel'man, Introduction To The Theory Of Atomic Spectra, Pergamon Press Oxford – New York – Toronto – Sydney – Paris – Braunschweig, (1972). [ Links ]
15. G. Wunner and H. Ruder, ApJ 242 (1980) 828. [ Links ]
16. C. Cuvelliez, D. Baye, and M. Vincke, Phys. Rev. A 46 (1992) 4055. [ Links ]
17. G.G. Pavlov and A.Y. Potekhin, ApJ. 450 (1995) 883. [ Links ]
18. A.Y. Potekhin, J. Phys. B 27 (1994) 1073. [ Links ]
19. A.Y. Potekhin, J. Phys. B 31 (1998) 49. [ Links ]
20. V.G. Bezchastnov, G.G. Pavlov and J. Ventura, Phys. Rev. A 58 (1998) 180. [ Links ]
21. A.Y. Potekhin and A.V. Turbiner, Phys. Rev. A 63 (2001) 065402. [ Links ]
22. A.R.P Rau and L. Spruch, ApJ 207 (1976) 671. [ Links ]
23. N.L. Khvingia and A.V. Turbiner, J. Phys. B 25 (1992) 343. [ Links ]
24. H.O. Pilón, Estudio de los estados más bajos del átomo de higrógeno en campos magnéticos y transiciones radiativas, MSc. Thesis (in spanish), UNAM, Mexico, (2007). [ Links ]














