Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
-
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO -
 Accesos
Accesos
Links relacionados
-
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Revista mexicana de física
versión impresa ISSN 0035-001X
Rev. mex. fis. vol.53 no.5 México oct. 2007
Investigación
Electroweak-Higgs unification in the two Higgs doublet model: masses and couplings of the neutral and charged Higgs bosons
J.L. Díaz-Cruzª y A. Rosadob
ª Facultad de Ciencias Físico-Matemáticas, BUAP, Apartado Postal 1364, 72000 Puebla, Pue., México.
b Instituto de Física, BUAP, Apartado Postal J-48, 72570 Puebla, Pue., México.
Recibido el 25 de mayo de 2007
Aceptado el 30 de agosto de 2007
Abstract
We obtain the mass spectrum and the Higgs self-couplings of the two Higgs doublet model (THDM) in an alternative unification scenario where the parameters of the Higgs potential λi (i = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) are determined by imposing their unification on the electroweak gauge couplings. An attractive feature of this scenario is the possibility of determining the Higgs boson masses by evolving the from the λi electroweak-Higgs unification scale MGH down to the electroweak scale. The unification condition for the gauge (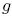 1,
1, 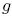 2) and Higgs couplings is written as
2) and Higgs couplings is written as 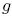 1 =
1 = 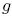 2 =ƒ(λi), where
2 =ƒ(λi), where 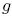 1 =
1 = 
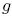 Y, and kY isthe normalization constant. Two variants for the unification condition are discussed: Scenario I is defined through the linear relation:
Y, and kY isthe normalization constant. Two variants for the unification condition are discussed: Scenario I is defined through the linear relation: 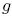 1 =
1 = 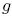 2 = kH(i) λi (MGH), while Scenario II assumes a quadratic relation
2 = kH(i) λi (MGH), while Scenario II assumes a quadratic relation 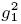 =
= 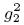 = kH(i) λi (MGH). In Scenario I, by setting ad hoc —kH (5) =
= kH(i) λi (MGH). In Scenario I, by setting ad hoc —kH (5) =  (4) =
(4) = 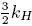 (3) = kH (2) = kH(1) = 1, taking tan β = 1 and using the standard normalization (kY = 5/3), we obtain the following spectrum for the Higgs boson masses:
(3) = kH (2) = kH(1) = 1, taking tan β = 1 and using the standard normalization (kY = 5/3), we obtain the following spectrum for the Higgs boson masses: 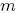 h°= 109.1 GeV,
h°= 109.1 GeV, 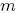 H°= 123.2 GeV,
H°= 123.2 GeV, 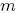 A°= 115.5 GeV, and
A°= 115.5 GeV, and 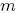 H± = 80.3 GeV, with similar results for other normalizations such as kY = 3/2 and kY = 7/4.
H± = 80.3 GeV, with similar results for other normalizations such as kY = 3/2 and kY = 7/4.
Keywords: Electroweak-Higgs unification; Higgs boson masses and couplings; Two Higgs doublet model.
Resumen
Se obtienen el espectro de masas y los autoacoplamientos de los bosones de Higgs en el modelo de dos dobletes de Higgs, en un escenario de unificacion alternativo donde los parámetros del potencial de Higgs λi (i = 1,2,3,4,5) son determinados imponiendo su unificación con los acoplamientos de norma electrodébiles. Una característica atractiva de este escenario es la posibilidad de determinar las masas de los bosones de Higgs mediante la evolucion de las λi,s de la escala de unificacion electrodébil-Higgs MGH a la escala electrodébil. La condición de unificación para los acoplamientos de norma (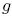 1,
1, 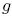 2) y de Higgs es
2) y de Higgs es 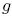 1 =
1 = 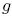 2 = ƒ(λi) , donde
2 = ƒ(λi) , donde 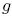 1 =
1 = 
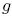 Y , y kY es la constante de normalización. Dos variantes para la condición de unificación son discutidas. Escenario I definido a través de la relación lineal:
Y , y kY es la constante de normalización. Dos variantes para la condición de unificación son discutidas. Escenario I definido a través de la relación lineal: 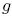 1 =
1 = 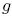 2 = kH (i) λi (MGH) , mientras en el Escenario II se supone una relación cuadrática:
2 = kH (i) λi (MGH) , mientras en el Escenario II se supone una relación cuadrática: 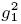 =
= 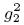 = kH (i) λi (MGH). Trabajando en el Escenario I, fijando ad hoc —kH (5) =
= kH (i) λi (MGH). Trabajando en el Escenario I, fijando ad hoc —kH (5) = (4) =
(4) = 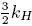 (3) = kH(2) = kH(1) = 1, tomando tan β = 1 y usando la normalización estándar (kY = 5/3), se obtiene el siguiente espectro de masas para los bosones de Higgs
(3) = kH(2) = kH(1) = 1, tomando tan β = 1 y usando la normalización estándar (kY = 5/3), se obtiene el siguiente espectro de masas para los bosones de Higgs h°= 109.1 GeV,
h°= 109.1 GeV,  H°= 123.2 GeV,
H°= 123.2 GeV, 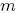 A° =115.5 GeV, y
A° =115.5 GeV, y 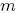 H ± = 80.3 GeV, con resultados similares para otras normalizaciones, tales como kY= 3/2 and kY = 7/4.
H ± = 80.3 GeV, con resultados similares para otras normalizaciones, tales como kY= 3/2 and kY = 7/4.
Descriptores: Unificación electrodébil-Higgs; masas y acoplamientos de bosones de Higgs; Modelo de dos dobletes de Higgs.
PACS: 12.60.Fr; 12.15.Mm; 14.80.Cp
DESCARGAR ARTÍCULO EN FORMATO PDF
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank CONACYT and SNI (México) for their financial support, and the Huejotzingo Seminar for inspiring discussions. J.L. Díaz-Cruz also wishes to thank A. Aranda for interesting discussions.
References
1. For a review of radiative corrections see: (LEP Collaborations), arXiv:hep-ex/0412015. [ Links ]
2. See also: P. Langacker, arXiv:hep-ph/0211065. [ Links ]
3. U. Baur et al. (The Snowmass Working Group on Precision Electroweak Measurements Collaboration), in Proc. of the APS/DPF/DPB Summer Study on the Future of Particle Physics (Snowmass 2001) ed. N. Graf, eConf C010630, P1WG1 (2001) (arXiv:hep-ph/0202001). [ Links ]
4. J.L. Diaz-Cruz, Mod. Phys. Lett. A 20 (2005) 2397; (arXiv:hep-ph/0409216). [ Links ]
5. For a review see: D.J.H. Chung et al., arXiv:hep-ph/0312378. [ Links ]
6. For a recent review of GUTs see: R.N. Mohapatra, hep-ph/0412050. [ Links ]
7. J.L. Diaz-Cruz, H. Murayama, and A. Pierce, Phys. Rev. D65 (2002) 075011; (arXiv:hep-ph/0012275). [ Links ]
8. J.L. Diaz-Cruz and J. Ferrandis, arXiv:hep-ph/0504094. [ Links ]
9. N. Arkani-Hamed, S. Dimopoulos, and G.R. Dvali, Phys. Lett. B429 (1998) 263. [ Links ]
10. I. Antoniadis, N. Arkani-Hamed, S. Dimopoulos, and G.R. Dvali, Phys. Lett. B436 (1998) 257. [ Links ]
11. D. Cremades, L.E. Ibanez, and F. Marchesasno, Nucl. Phys. B643 (2002) 93. [ Links ]
12. C. Kokorelis, Nucl. Phys. B677 (2004) 115. [ Links ]
13. L. Randall and R. Sundrum, Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 (1999) 3370. [ Links ]
14. N. Arkani-Hamed and M. Schmaltz, Phys. Rev. D61 (2000) 033005; (arXiv:hep-ph/9903417). [ Links ]
15. R. Barbieri, P. Creminelli, and A. Strumia, Nucl. Phys. B585 (2000) 28; (arXiv:hep-ph/0002199). [ Links ]
16. N. Arkani-Hamed, S. Dimopoulos, G.R. Dvali, and I March-Russell, Phys. Rev. D65 (2002) 024032; (arXiv:hep-ph/9811448). [ Links ]
17. R.N. Mohapatra and A. Perez-Lorenzana, Phys. Rev. D66 (2002) 035005; (arXiv:hep-ph/0205347). [ Links ]
18. N. Cosme et al., Phys. Rev. D63 (2001) 113018; (arXiv:hep-ph/0010192). [ Links ]
19. A. Ioannisian and J.W.F. Valle, Phys. Rev. D 63 (2001) 073002; (arXiv:hep-ph/9911349). [ Links ]
20. A. Aranda, C. Balazs, and J.L. Diaz-Cruz, Nucl. Phys. B670 (2003) 90; (arXiv:hep-ph/0212133). [ Links ]
21. A. Aranda and J.L. Diaz-Cruz, Mod. Phys. Lett. A20 (2005) 203; (arXiv:hep-ph/0207059). [ Links ]
22. K.R. Dienes, E. Dudas, and T. Gherghetta, Phys. Lett. B436 (1998) 55. [ Links ]
23. L. J. Hall, Y. Nomura, and D.R. Smith, Nucl. Phys. B639 (2002) 307; (arXiv:hep-ph/0107331). [ Links ]
24. See for instance the so-called fat Higgs models: R. Harnik et al., Phys. Rev. D70 (2004) 015002. [ Links ]
25. For a review of little Higgs models see: Jay G. Wacker, arXive: hep-ph/0208235. [ Links ]
26. For models with composite Higgs using AdS-CFT duality see: K. Agashe, R. Contino, and A. Pomarol, Nucl. Phys. B719 (2005) 165. [ Links ]
27. A. Aranda, J.L. Diaz-Cruz, and A. Rosado, arXiv:hep-ph/0507230 (to be published in Int. Jour. Mod. Phys. A). [ Links ]
28. N.S. Manton, Nucl. Phys. B158 (1979) 141. [ Links ]
29. D.B. Fairlie, Phys. Lett. B 82 (1979) 97. [ Links ]
30. I. Antoniadis, K. Benakli, and M. Quiros, New J. Phys. 3 (2001) 20; (arXiv:hep-th/0108005). [ Links ]
31. Y. Hosotani, S. Noda, and K. Takenaga, Phys. Lett. B607 (2005) 276; (arXiv:hep-ph/0410193). [ Links ]
32. C. Csaki, C. Grojean, and H. Murayama, Phys. Rev. D67 (2003) 085012; (arXiv:hep-ph/0210133). [ Links ]
33. Y Hosotani, S. Noda, and K. Takenaga, Phys. Lett. B607 (2005) 276; (arXiv:hep-ph/0410193). [ Links ]
34. C.A. Scrucca, M. Serone, L. Silvestrini, and A. Wulzer, JHEP 0402 (2004) 049; (arXiv:hep-th/0312267). [ Links ]
35. C. A. Scrucca, M. Serone, and L. Silvestrini, Nucl. Phys. B 669 (2003) 128; (arXiv:hep-ph/0304220). [ Links ]
36. G. Burdman and Y Nomura, Nucl. Phys. B 656 (2003) 3; (arXiv:hep-ph/0210257). [ Links ]
37. N. Haba and Y Shimizu, Phys. Rev. D 67 (2003) 095001; (Erratum-ibid. D 69 (2004) 059902); (arXiv:hep-ph/0212166). [ Links ]
38. I. Gogoladze, Y Mimura, and S. Nandi, Phys. Lett. B 560 (2003) 204; (arXiv:hep-ph/0301014). [ Links ]
39. I. Gogoladze, Y Mimura, and S. Nandi, Phys. Lett. B 562 (2003) 307; (arXiv:hep-ph/0302176). [ Links ]
40. I. Gogoladze, Y Mimura, and S. Nandi, Phys. Rev. D 69 (2004) 075006; (arXiv:hep-ph/0311127). [ Links ]
41. I. Gogoladze, Y Mimura, and S. Nandi, Phys. Lett. B560 (2003) 204; (arXiv:hep-ph/0301014). [ Links ]
42. I. Gogoladze, T. Li, Y Mimura, and S. Nandi, Phys. Rev. D 72 (2005) 055006; (arXiv:hep-ph/0504082). [ Links ]
43. K.R. Dienes and J. March-Russell, Nucl. Phys. B 479 (1996) 113; (arXiv:hep-th/9604112). [ Links ]
44. V. Barger, J. Jiang, P. Langacker, and Y Li, Nucl. Phys. B726 (2005) 149. [ Links ]
45. V. Barger, M.S. Berger, and M.S. Ohman, Phys. Rev. D47 (1993) 1093. [ Links ]
46. Review of Particle Physics. Particle data group. Phys. Lett. B592 (2004)1. [ Links ]
47. The values for the top mass used here are based in the data recently reported in: A. Abulencia et al. (CDF Collaboration), "Measurement of the top quark mass using template methods on dilepton events in proton antiproton collisions at s**(1/2) = 1.96-TeV," arXiv:hep-ex/0602008. [ Links ]
48. See also: A. Abulencia et al. (CDF Collaboration), "Top quark mass measurement from dilepton events at CDF II with the matrix-element method," arXiv:hep-ex/0605118. [ Links ]
49. M. Duhrssenet et al.,Phys. Rev. D 70 (2004) 113009; (arXiv:hep-ph/0406323). [ Links ]
50. J.L. Diaz-Cruz and D.A. Lopez-Falcon, Phys. Lett. B 568 (2003) 245; (arXiv:hep-ph/0304212). [ Links ]
51. D. Kominis and R. Sekhar, Phys. Lett. B304 (1993) 152. [ Links ]
52. J.L. Diaz-Cruz and A. Mendez, Nucl. Phys. B380 (1992) 39. [ Links ]
53. J. Gunion, H. Haber, G. Kane, and S. Dawson, The Higgs Hunter's Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishig Company, Reading, MA, 1990). [ Links ]
54. (ALEPH Collaboration), arXiv:hep-ex/0602042. [ Links ]
55. R. Barate et al., (LEP Working Group for Higgs boson searches), Phys. Lett. B 565 (2003) 61; (arXiv:hep-ex/0306033). [ Links ]
56. A. Heister et al., (ALEPH Collaboration), Phys. Lett. B 543 (2002) 1; (arXiv:hep-ex/0207054). [ Links ]
57. C. Balazs, J.L. Diaz-Cruz, H.J. He, T. Tait, and C.P Yuan, Phys. Rev. D 59 (1999) 055016; (arXiv:hep-ph/9807349). [ Links ]
58. J.L. Diaz-Cruz, H.J. He, T. Tait, and C.P. Yuan, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 (1998) 4641; (arXiv:hep-ph/9802294). [ Links ]
59. N. Arkani-Hamed and S. Dimopoulos, arXiv:hep-th/0405159. [ Links ]
60. M.J.G. Veltman, Acta Phys. Polon. B12 (1981) 437. [ Links ]














