Servicios Personalizados
Revista
Articulo
Indicadores
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO  Accesos
Accesos
Links relacionados
 Similares en
SciELO
Similares en
SciELO
Compartir
Revista mexicana de ciencias geológicas
versión On-line ISSN 2007-2902versión impresa ISSN 1026-8774
Resumen
MIRANDA-MARTINEZ, Ma. Eugenia et al. Porosity in naturally fractured media: A fractal classification. Rev. mex. cienc. geol [online]. 2006, vol.23, n.2, pp.199-214. ISSN 2007-2902.
The flow and distribution of fluids through pores in porous media are governed by their geometry. The self-similar behavior of the structure of these sets has been the subject of numerous studies that have documented the power laws relationship, among the principal measures of pores and solids, and the resolution of the method used for their analysis. A fractal scheme is introduced in order to extract and measure some geometric features of pores, using the mean values of their fractal classifiers, dividing these in global (ftrmagram) and local (reference line) classifiers. The mass fractal dimension (Dm), the spectral dimension orfracton (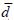 ), the Hurst exponent (H) and the lacunarity (Λ) of naturally fractured reservoirs (YNF) of southeastern Mexico, have shown to be statistically different for the three most representative porosity sets: fractures, cavities and mixed porosity. The fractal classifiers, extracted from digital images obtained using X-ray computerized tomography, were useful for porosity classification in different patterns, starting from the core images. Dm and
), the Hurst exponent (H) and the lacunarity (Λ) of naturally fractured reservoirs (YNF) of southeastern Mexico, have shown to be statistically different for the three most representative porosity sets: fractures, cavities and mixed porosity. The fractal classifiers, extracted from digital images obtained using X-ray computerized tomography, were useful for porosity classification in different patterns, starting from the core images. Dm and 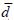 must be determined on presegmented images, which distinguish the pore and solid sets, prior to the fractal quantification, while H and Λ can be extracted from the original image, which drastically diminishes the bias in the porosity estimation. All fractal classifiers, including mass dimensions and lacunarity of the porosity patterns specified above for YNF, showed a statistically significant correlation with the porosity of the geological strata as determined by traditional techniques. All our results offer new perspectives for the modeling and forecasting of porosity in the naturally fractured deposits.
must be determined on presegmented images, which distinguish the pore and solid sets, prior to the fractal quantification, while H and Λ can be extracted from the original image, which drastically diminishes the bias in the porosity estimation. All fractal classifiers, including mass dimensions and lacunarity of the porosity patterns specified above for YNF, showed a statistically significant correlation with the porosity of the geological strata as determined by traditional techniques. All our results offer new perspectives for the modeling and forecasting of porosity in the naturally fractured deposits.
Palabras llave : fractal dimension; X-ray tomography; digital images; structure; porosity; fractured media.














