The International Program of Student Evaluation (Programa Internacional de Evaluación de Estudiantes [PISA], in Spanish), defines students with “low achievement” as those that obtain grades lower than Level 2 in the PISA exams for math, reading and science, provided Level 2 is considered the basic level of knowledge required to fully participate in a modern society. Mexico has a very high percentage of Level 2 students in science, mathematics and reading (47.8, 56.6, and 41.7, respectively), which locates them well above the levels of the whole OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) (21.2, 23.4, and 20.1 respectively) and the United States of America (20.3, 29.4 and 19 respectively) (OECD, 2018).
Academic achievement is a multidimensional variable that is related to structural (i.e., group size) (Rué et al., 2013), economic (i.e., family income) (Baoyan & Minggang, 2015; Chittleborough et al., 2014), pedagogical (i.e., type of teaching) (Ahmad et al., 2017; Guirguis & Pankowski, 2017), educational (i.e., previous GPA) (Cortés Flores & Palomar Lever, 2008; Geiser & Santelices, 2007; Pike & Saupe, 2002) and psychosocial factors (i.e., family support) (Shahed et al., 2016). The importance of researching academic achievement lies in its predictive power of social and occupational insertion (Flores-Crespo, 2002; Villarreal Guevara et al., 2009), higher income (Carrillo Regalado & Ríos Almodóvar, 2013; Post & Pong, 2009) and better quality of life (INEE, 2015).
The influence each of these factors have on academic achievement vary according to the different education levels students are attending. In basic education for instance, academic achievement is heavily influenced by parental support and supervision, while in high school and college, tutor supervision of compliance to academic goals is lower and more dependent on individual factors (Bornstein, 2002; Camacho-Thompson, Gillen-O'Neel, Gonzales, & Fuligni, 2016).
In practice, the vast majority of research destined to explain academic success or failure, measure academic achievement through the Grade Point Average or student academic certification (Tejedor, 2003). Achievement is defined as the process through which a person acquires knowledge, aptitudes, abilities, attitudes and skills. It supposes an adaptive chance and is a result of environmental interaction (Canda, 2010).
Within individual factors that affect academic achievement, personality traits have been the least explored. There is evidence that suggest some personality traits influence academic achievement (Banai & Perin, 2016; Poropat, 2011). Explicitly: responsibility, neuroticism and self-efficacy have been indicated as contributors in explaining academic achievement (Stajkovic, Bandura, Locke, Lee, & Sergent, 2018); nonetheless there are doubts about the replicability of these findings in different populations given that academic, structural and interpersonal conditions vary across students and cultures (e.g., Marconi, 2015) mentions that the average number of pupils in a United States classroom is 16, while in Mexico the average number of pupils is 35. In order to understand achievement, it is also essential to address interpersonal relationships within a sociocultural environment given that they include among other things, the level of agreement with cultural premises which might vary from culture to culture (Palacios & Martínez, 2017).
Personality traits that influence academic achievement
Neuroticism is a negative predictor of academic achievement. Stress, impulsiveness and anxiety are behaviors that are related to neuroticism and can influence academic achievement (Chamorro-Premuzic & Furnham, 2002). Responsibility is due to the motivational properties of this factor that is reflected in the effort and persistence that students with high levels of this trait report (Chamorro-Premuzic & Furnham, 2003). Openness is positively associated to academic achievement through tasks of verbal communication, language and math (Gargurevich & Soenens, 2016). Agreeableness might have a positive impact on academic achievement given that it facilitates cooperation during the learning process (De Raad & Schouwenburg, 1996). Extraversion has been negatively associated to academic achievement given that it suggests that introverts spend more time studying while extroverts spend more of their time socializing (Chamorro-Premuzic & Furnham, 2005). Honesty and humility is divided into 4 dimensions (Lee & Ashton, 2004), sincerity (the tendency towards sincerity and not manipulative), equity (the tendency to follow impartiality and integrity), greed aversion (low luxury and commodity greed) and modesty (low levels of feelings of superiority and entitlement). De Vries, De Vries and Born (2011) demonstrated the utility of the honesty-humility dimensions to predict GPA.
Personality traits predispose individuals to engage in behavior paterns that are coherent with the traits, and can also result in higher self-efficacy towards those same activities given the repetitive practice, somewhat like the concept of approved domain. Self-efficacy is not obliged by personality traits. Given that self-efficacy depends on the experience an individual has with a particular challenge, it is adaptable and can be enhanced through the decreed domain, indirect learning and verbal persuasion. In other words: it is the students’ perception of the characteristics in their social environment such as impediments and opportunities that influence their actions. Those with low self-efficacy convince themselves of the futility behind their efforts when facing academic obstacles, while those with high self-efficacy find the way to overcome them (Stajkovic et al., 2018).
Brown, Lent, Telander, and Tramayne (2011) fond that the Big Five significantly correlated with both academic achievement and self-efficacy, and in contrast to previous literature, self-efficacy also correlated with achievement (Caprara, Vecchione, Alessandri, Gerbino, & Barbaranelli, 2011; Pérez, Cupani, & Ayllón, 2005).
Personality traits that influence self-efficacy
Self-efficacy has been substantially related to some personality traits, particularly to extraversion, openness and responsibility, while demonstrating no relation with agreeableness (Judge & Ilies, 2002). Self-efficacy is an important mediator of the responsibility-performance relationship. Responsibility is a trait that includes general motivation tendencies, involves the degree to which an individual is efficient, hard-working and dedicated (Chen, Casper, & Cortina, 2001). Self-efficacy suggests that when people are willing to undergo new experiences (openness), it might be partly due to a higher feeling of self-efficacy, which also increases their compromise (Sanchez-Cardona et al., 2012). Extraversion is a personality trait that reflects qualties such as excitation, sociability, high energy and positive emotion. High levels of excitation (high energy), found in extroverted individuals also coincided with high levels of self-efficacy (Esfandagheh, Harris, & Oreyzi, 2012). In contrast, people with high levels of neuroticism lack self-confidence and do not believe in their capabilities to perform tasks effectively (Thoms, Moore, & Scott, 1996).
The influence of self-efficacy in academic achievement
Academic self-efficacy is understood as personal beliefs about the capabilities of organizing and executing actions to reach the desired levels of academic achievement (Zimmerman, 1995). In academic self-efficacy, beliefs are positively related to performance, achievement and effort. The relation between self-efficacy with academic achievement varies according to the level of student achievement, between those students with low levels of achievement and those that have an expected level of academic achievement. This suggests how the effects of self-efficacy can act as a facilitator for those students with low levels of achievement by aiming to value development and evaluation in order to promote the perceptions of academic self-efficacy among these students (Multon et al., 1991). Bandura (1977) specifies that perceived academic self-efficacy is defined as personal judgements about the individual’s capabilities to organize and execute courses of action in order to reach designed types of academic achievements.
According to cognitive theory, self-efficacy influences the election of behavioral responses, cognitive patterns and emotional responses, it determines the effort individuals invest in an activity and how persevering they will be when facing obstacles, allowing the individual to produce their own future and not only predict it (Caballero, Abello, & Palacio, 2007).
Perceived self-efficacy has a central place in the causal structure of cognitive theory as beliefs of self-efficacy affect adaptation. Such beliefs influence individuals to have a more pessimistic or optimistic way of thinking and the ways in which they hamper or better themselves (Usher & Pajares, 2006). Efficacy beliefs also play a central role in motivation self-regulation through challenges and result expectations. In social cognitive theory, socio-structural factors operate through psychological mechanisms in the self that produce behavioral effects (Bandura, 2001).
The mediating role of self-efficacy in behavior is developed through four sources: domain experience (i.e. students with higher GPAs develop a strong sense of self-confidence towards their capabilities), vicarious experience (i.e., effects produced by the actions of others), social persuasions (i.e., messages that are received from other favoring self-efficacy beliefs) and physiological states associated to anxiety, tension, excitation, fatigue and mood (i.e., individuals estimate their levels of confidence based on the mood they experience when doing an action) (Bandura in Usher & Pajares, 2006). Self-efficacy plays an important role in the prediction of academic achievement (Multon, Brown, & Lent, 1991; Zimmerman, 1995), while personality traits also help shape achievement in an individual (de Vrieset al., 2011; Poropat, 2009).
Three conceptual models of joint influences
Stajkovic et al. (2018) examined joint variables of the Big Five and self-efficacy as part of a conceptual model with mixed findings. They put to the test three conceptual models about the influence certain variables have on college academic achievement throughout a semester given that there was an active interest in the participants to better understand their achievement. The study collected data from five different samples enrolled in three universities from two different countries N=875 and performed a meta-analysis on student academic paths. Controlling for general mental ability (GMA) and considered GPA as achievement. Results show that self-efficacy is positively related to academic achievement in all models that specified this relationship, while responsibility and mental stability (neuroticism) predicted self-efficacy and academic achievement in some analyses.
1. Trait model
In this model, the impact personality traits, self-concept and middle school GPA have on highschool GPA are mediated by self-efficacy (Fig. 1). The mediating role of self-efficacy is based on the claim that self-efficacy represents a mechanism through which generalized tendencies are expressed (Stajkovic et al., 2018).
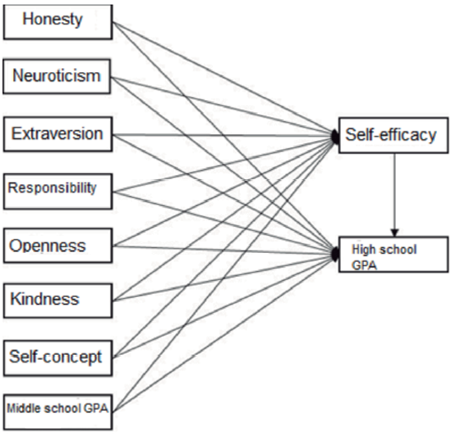
Figure 1 Trait model. The endogenous variables are Honesty, Neuroticism, Extraversion, Responsibility, Openness, Kindness, Self-concept and middle school GPA. The exogenous variables are shown through standardized estimations: Self-efficacy and high school GPA (Academic achievement). Adapted from “Test of three conceptual models of influence of the big five personality traits and self-efficacy on academic performance: A meta-analytic path-analysis” (Stajkovic et al., 2018). Personality and Individual Differences. Copyright (2018) Elsevier Ltd.
2. Independent model
In this model (Fig. 2), personality traits, self-concept and middle school GPA influence both academic achievement and self-efficacy independently, without a mediatory path from self-efficacy to academic achievement. This model is based on the findings about the effects of self-efficacy in academic achievement (Stajkovic et al., 2018).
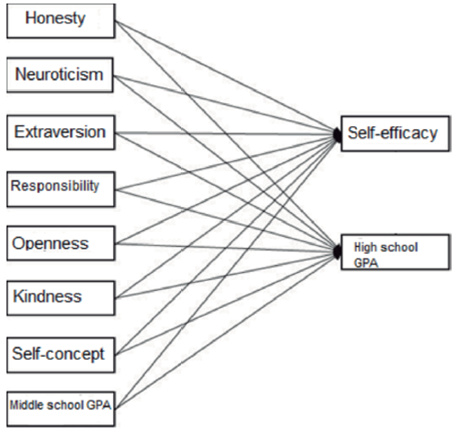
Figure 2 Independent model. The endogenous variables are Honesty, Neuroticism, Extraversion, Responsibility, Openness, Kindness, Self-concept and middle school GPA. The exogenous variables are shown through standardized estimations: Self-efficacy and high school GPA (Academic achievement). Adapted from “Test of three conceptual models of influence of the big five personality traits and self-efficacy on academic performance: A meta-analytic path-analysis” (Stajkovic et al., 2018). Personality and Individual Differences. Copyright (2018) Elsevier Ltd.
3. Intrapersonal model
In this model (Fig. 3), the effect personality traits have on highschool GPA is indirect and mediated by self-efficacy. Given that academic achievement occurs dynamically in different content areas and under a plethora of circumstances, previous studies are not clear enough as to demonstrate that personality traits are effective as non-conditional generalities to predict academic achievement variance as opposed to self-efficacy (Stajkovic et al., 2018).
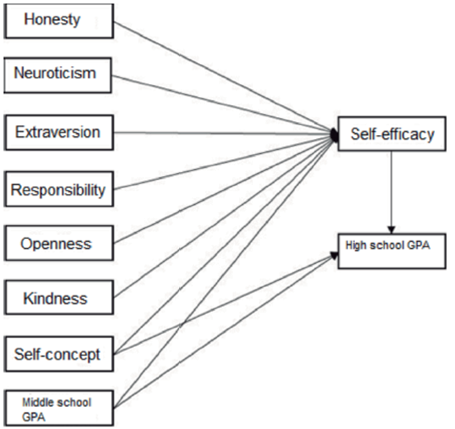
Figure 3 Intrapersonal model. The endogenous variables are Honesty, Neuroticism, Extraversion, Responsibility, Openness, Kindness, Self-concept and middle school GPA. The exogenous variables are shown through standardized estimations: Self-efficacy and high school GPA (Academic achievement). Adapted from “Test of three conceptual models of influence of the big five personality traits and self-efficacy on academic performance: A meta-analytic path-analysis” (Stajkovic et al., 2018). Personality and Individual Differences. Copyright (2018) Elsevier Ltd.
Although both personality traits and self-efficacy have been studied separate and jointly, there is still no clear explanation on how other personality traits and self-efficacy interact to influence academic achievement. There is very little evidence of research done in Mexico about the existing interrelations between personality traits, self-efficacy, self-concept and academic achievement in high school students, and that is why his research project is relevant.
Aiming to further comprehend the characteristics that contribute to high school academic achievement in Mexican youth, the individual and joint contributions of personality traits and self-efficacy to academic achievement were based on the three conceptual Path Analysis models of academic achievement proposed by Stajkovic, et al, (2018) while also adding academic self-concept and previous academic achievement (middle school GPA). We included self-concept because it is related to academic success, student health and long term wellbeing (Cooperation, Development, & Statistics, 2003), while also performing a critical role in academic interest and satisfaction among students by underpinning their academic achievements (Marsh & Martin, 2011). We also included middle school GPA given that various studies (Choi, 2005; Cortés Flores & Palomar Lever, 2008; Marsh & Martin, 2011; Moreano, 2005) have emphasized its role as predictor of highschool GPA. We did not include a general mental ability measure as both Grigorenko et al. (2009) and Stajkovic et al. (2018) have shown that middle school GPA is the best predictor of highschool academic achievement even when compared to the SSAT (Secondary School Admission Test).
Method
Sample
During spring 2017, the PI approached the authorities of a public high school in the western part of Mexico City to ask for their permission to approach students and parents, and consequently send informative documents about the reaches, potential risks, confidentiality and anonymity in the research process and collect data. Data recollection began June 2017, where students enrolled in the last semester of high school from both morning and afternoon shifts signed an informed consent and then filled out an electronic questionnaire through SurveyMonkey® in the computer classrooms of the school.
The application was approximately 45 minutes long, participants were asked to answer the scales in the most clear and sincere way possible. Throughout the process, response anonymity was emphasized and the participants were reminded that their responses would not be judged as incorrect, nor would they help or impair them in any way.
Our analytic sample was comprised by 725 Mexican public high school students enrolled in the last semester of high school in both morning and afternoon shifts with an age range between 17 and 23 years of age which is normal for public high schools in Mexico as the last level of education concluded for the average Mexican is middle school (M = 18, SD = 1.09), 291 males, 434 females.
Measurements
The online self-report that was answered by students consisted of a sociodemographic questionnaire and five scales. Questions regarding their current GPA, their middle school GPA were added as well. Once participants entered the computer classroom, they were reminded about both the anonymity and confidentiality of the research process and were explicitly told this would not affect their current GPA in any way. There were no missing values, as the PI specified the electronic platform to not allow the submission of the questionnaire if there were missing data. The scales we used were:
Self-efficacy scale (Owen & Froman, 1988) adapted by Becerra- González and Reidl (2015) into Spanish. The original scale consists of 31 items responded by a 4 point Likert type scale ranging from 1 (not self-efficacious at all) to 4 (I feel completely efficacious) (e.g. take organized notes in class, do a test, ask the teacher about something that was not clear to you, paying careful attention in a class about a hard topic) where higher scores are indicative of higher self-efficacy.
The Academic Self-Concept Scale for Adolescents (Ordaz-Villegas, Acle-Tomasini, & Isabel Reyes-Lagunes, 2013) consists of 28 items answered by a 5 point Likert type scale ranging from 1 (never) to 5 (always) (e.g., Before beginning a task, I analyze the different ways to carry it out, I verbally express my ideas in a clear manner, I read and re-read a text many times to fin the principal idea, When I encounter a problem I find new strategies to solve it) higher scores mean higher academic self-concept.
HEXACO-Personality Inventory Revised (Lee & Ashton, 2004) which evaluates six personality dimensions: Honesty-humility, Emotionality (Neuroticism), Extraversion, Agreeableness, Conscientiousness and Openness to experience (e.g., I would be very bored if I visited an art gallery, I plan ahead and organize things to avoid rushing, I rarely resent people, even towards those that have offended me, I feel pretty satisfied with myself, I would be afraid to travel in bad weather, I would not use flattery to obtain a better GPA). The inventory has 60 items that are answered by a 5 point Likert type scale ranging from 1 (Strongly disagree) to 5 (Totally agree). The total internal consistency was α = .82, the internal consistencies for the dimensions were as follows: Honesty-humility α = .62, Emotionality (Neuroticism) α = .61, Extraversion α = .71, Agreeableness α = .58, Conscientiousness α = .68 and Openness to experience α = .67.
Academic achievement was measured through self-reported GPA for the last semester of high school. This measurement could not be extracted from the institution’s system for confidentiality reasons.
Middle school academic achievement was measured through self-reported middle school GPA for the same reasons as high school GPA.
Analysis
The study began with internal consistency and exploratory factor analyses in order to derive valid and reliable measures of the different constructs. Items with low explained variances and communalities across all scales were eliminated and thus the remaining items and resulting factorial structure had to be analyzed. All factors were extracted using principal components analysis, both the self-efficacy scale and the academic self-concept scale structures were constrained to one factor for parsimony reasons. The EFA on the HEXACO inventory followed Kaiser’s criterion with varimax rotation.
Using SPSS, descriptive statistics were used to obtain information about the sample’s characteristics. In order to find out the level participants were in related to the variables, measures of central tendency and dispersion were calculated. Relationships between variables were analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Furthermore, the three conceptual models of influence for personality traits and/or self-efficacy on academic achievement (Stajkovic et al., 2018) were replicated through Path Analyses in AMOS. All three models were specified by adding covariances between all endogenous variables, coefficients were computed using Maximum Likelihood estimation.
Results
After performing exploratory factor analyses, our obtained self-efficacy scale consisted of 26 items grouped in a single dimension (KMO = .92, significant sphericity, and 33% of explained variance) with high internal consistency (α = .93). Similarly, our obtained academic self-concept scale consisted of 26 items arranged in a single dimension with high internal consistency (α = .91, KMO = .93, significant sphericity, and 35% of explained variance). With the exception of HEXACO’s agreeableness scale, all personality trait subscales presented internal consistencies higher than α=.6, which suggests adequate reliability across all our measures. Although variables were not normally distributed, skewness and kurtosis absolute values were not over the absolute value thresholds (2 and 6 respectively) that would suggest the need for data transformation before the analyses.
It was observed that students enrolled in the afternoon shift were significantly older given that some of them work during the mornings due to economic reasons t(524.5) = 45.35*** Cohen’s d = .30. Additionally, students enrolled in the afternoon shift had significantly worse high school academic achievement when compared to the morning shift t(722.05) = 4.13*** Cohen’s d = .31. Measures of central tendency, dispersion and distribution are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Univariate properties of the main variables related to academic achievement in Mexican high school students.
| M | SD | Rank | Skewness | Kurtosis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potential | Real | |||||
| High school Academic Achievement | 8.03 | 0.69 | 5 - 10 | 0 -10 | 0.17 | -0.32 |
| Self-efficacy | 2.89 | 0.49 | 1 - 4 | 1.44 - 4 | 0.02 | -0.22 |
| Academic self-concept | 3.39 | 0.64 | 1 - 5 | 1.73 - 5 | -0.31 | -0.35 |
| Middle school GPA | 8.8 | 0.75 | 5 - 10 | 0 - 10 | -0.57 | -0.17 |
| Personality traits | ||||||
| Honesty-Humility | 3.34 | 0.61 | 1 - 5 | 1.5 - 5 | 0.13 | 0.08 |
| Emotionality (Neuroticism) | 3.07 | 0.58 | 1 - 5 | 1.1 - 4 | -0.11 | 0.02 |
| Extraversion | 3.3 | 0.62 | 1 - 5 | 1 - 5 | -0.19 | 0.49 |
| Agreeableness | 2.97 | 0.56 | 1 - 5 | 1.3 - 4.9 | -0.07 | 0.33 |
| Conscientiousness | 3.33 | 0.6 | 1 - 5 | 1.6 - 5 | 0.21 | -0.07 |
| Openness to Experience | 3.42 | 0.59 | 1 - 5 | 1.3 - 5 | 0.12 | -0.44 |
Note: n= 725
A correlation analysis between all variables was run in order to verify the level of connection among them. The variables that presented the highest correlations with high school academic achievement were: Middle school GPA (r = .48**), Conscientiousness (r = .29**) and Self-efficacy (r = .26**). Self-efficacy was significantly correlated with Academic self-concept (r = .74**), Extraversion (r = .43**), Conscientiousness (r = .43**) and negatively correlated to Emotionality (Neuroticism) (r = -.08*). Conscientiousness if highly correlated to Academic self-concept (r = .46**).
Table 2 Correlations between academic performance, self-efficacy and other predictive variables
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | High school Academic Achievement | - | |||||||||
| 2 | Academic self-concept | .17** | - | ||||||||
| 3 | Self-efficacy | .26** | .74** | - | |||||||
| 4 | Honesty/Humility | .14** | .09* | .05 | - | ||||||
| 5 | Emotionality (Neuroticism) | .12** | -.08* | -.08* | .06 | - | |||||
| 6 | Extraversion | .12** | .4** | .44** | 0 | -.05 | - | ||||
| 7 | Agreeableness | .05 | .15** | .12** | .23** | .05 | .15** | - | |||
| 8 | Conscientiousness | .29** | .46** | .43** | .28** | -.06 | .33** | .12** | - | ||
| 9 | Openness | .08* | .26** | .24** | .20** | .06 | .21** | .14** | .26** | - | |
| 10 | Secondary school GPA | .48** | .11** | .15** | .17** | .08* | .12** | .10** | .21** | .07 | - |
Note: * p<.05, ** p<.01
In Table 3, standardized regression weights (paths) across the three models are presented. Neuroticism and Conscientiousness were the only personality traits that were significant predictors of high school academic achievement. For both the trait and intrapersonal models, self-efficacy was a significant predictor of high school academic achievement; being that Extraversion and Academic self-concept were the only variables that significantly predicted self-efficacy, there was evidence of a possible mediation effect where self-efficacy intervened in a possible indirect effect from Extraversion and Academic self-concept on high school academic achievement.
Table 3 Standardized regression weights between variables across models
| Criterion variable | Predictor variable | Trait model | Independent model |
Intrapersonal model |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-efficacy | <-- | Honesty-Humility | -.03 | -.03 | -.03 |
| Self-efficacy | <-- | Emotionality (Neuroticism) | -.02 | -.02 | -.02 |
| Self-efficacy | <-- | Extraversion | .15** | .16** | .16** |
| Self-efficacy | <-- | Conscientiousness | .07 | .07 | .08 |
| Self-efficacy | <-- | Openness to Experience | .02 | .02 | .03 |
| Self-efficacy | <-- | Agreeableness | -.01 | -.01 | -.01 |
| Self-efficacy | <-- | Academic self-concept | .64** | .64** | .64** |
| Self-efficacy | <-- | Middle school GPA | .05 | .04 | .05 |
| High school Academic Achievement | <-- | Honesty-Humility | .02 | .01 | . |
| High school Academic Achievement | <-- | Emotionality (Neuroticism) | .11** | .1* | . |
| High school Academic Achievement | <-- | Extraversion | -.04 | 0 | . |
| High school Academic Achievement | <-- | Conscientiousness | .2** | .19** | . |
| High school Academic Achievement | <-- | Openness to Experience | -.03 | -.02 | . |
| High school Academic Achievement | <-- | Agreeableness | -.02 | -.03 | . |
| High school Academic Achievement | <-- | Academic self-concept | -.1 | .05 | -.06 |
| High school Academic Achievement | <-- | Middle school GPA | .41** | .43** | .45** |
| High school Academic Achievement | <-- | Self-efficacy | .23** | . | .24** |
Note:* p<.05, ** p<.01
Different Sobel tests with Bonferroni’s adjustment were performed in order to quantify the indirect effects Extraversion and Academic self-concept had over high school academic achievement when mediated by self-efficacy. The unstandardized paths and standard errors were combined and determined significant through a Wald test. Both models presented the same standardized indirect effects on high school academic achievement (Extraversion β = .04*** and Self-concept β = .15***) thus rendering self-efficacy as a significant mediator.
As to the comparison between the Path Analysis models based on Stajkovic et al. (2018), the trait model is a specified and saturated model meaning it presents perfect fit statistics by default. In contrast, both the independent and intrapersonal models are unsaturated, therefore they are conceptually more parsimonious than the trait model. In Table 4, it can be seen that the trait model was slightly more effective in explaining high school academic achievement (R² = . 30), while the level of explanatory power for self-efficacy was almost identical across all models. All models explain more self-efficacy variance than academic achievement variance given that academic self-concept is a more significant predictor of self-efficacy than of high school academic achievement. Previous academic achievement (middle school GPA) was the best predictor for high school academic achievement. The path between self-efficacy and high school academic achievement can be explained by a variation of 33% and 34% in the trait and intrapersonal models respectively, nonetheless this does not affect the independent model where this path is non-existent.
Table 4 Fit statistics across all models
| Trait model | Independent Model | Intrapersonal Model | |
|---|---|---|---|
| R² Self-efficacy | .59 | .59 | .58 |
| R² High school Academic Achievement | .3 | .28 | .27 |
| df | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| χ² | . | 23.3*** | 33.41*** |
| CFI | 1 | .96 | .98 |
| TLI | 1 | .32 | .86 |
| RMSEA | .21 (.2-.22) | .17*** (.11-.24) | .07* (.05-.11) |
| SRMR | .00 | .01 | .02 |
| AIC | 110 | 131.27 | 131.41 |
| BIC | 362.23 | 378.92 | 356.14 |
Note: * p<.05, ** p<.01, *** p<.001.
As to model comparison, the trait model was only directly comparable to the other two models through Akaike’s and Schwarz’s Bayesian Information Criteria given that it presented perfect fit indexes by default. Although the trait model presented the lowest AIC, the RMSEA was beyond the .05 threshold, indicating the model’s close fit was poor and therefore implying the absolute fit was deficient as well. A chi-squared test between the intrapersonal and independent model rendered marginally significant results (Δχ2(5) = 10.11 p < .10), meaning both models fit the data similarly. When compared to the independent model, the intrapersonal model presented higher values for both the CFI and TLI, similar values for the AIC, a lower BIC and an RMSEA that contains the .05 threshold value in its confidence interval and thus was chosen as our final model.
Discussion
Amidst the findings of this study, the model comparison supports the intrapersonal model as our final model given that it provides a more parsimonious explanation of the existing relationship between the present variables for Mexican public high school students. Despite the fact that structural and academic conditions in high schools are not the same in the United States and Mexico, this study shows similarities to the study carried out by Stajkovic et al. (2018) as middle school GPA, self-efficacy, neuroticism and conscientiousness were significant predictors of high school academic achievement in this study as well. As opposed to the independent and trait models, the intrapersonal model supports the relationship between self-efficacy and high school academic achievement while subtracting the direct effects personality traits have on academic achievement, thus resulting in a mediation effect between traits and achievement through self-efficacy.
The squared multiple correlations for both criterion variables across all three models were very similar and the three models explained a higher proportion of self-efficacy as opposed to high school academic achievement due that academic self-concept is a much stronger predictor of self-efficacy. Even though the link between self-efficacy and high school academic achievement adds a very small proportion to the trait and intrapersonal models explanatory power of academic achievement, the independent model was not the best fitting model and therefore disproved previous claims where personality traits are not mediated by self-efficacy (Chen, Casper & Cortina, 2001). An important difference between the independent and the trait model is that when the path from self-efficacy to high school academic achievement is absent (independent model), the path coefficients from both conscientiousness and neuroticism to academic achievement actually are smaller than those reported in the trait model, which also supports the mediation of personality traits through self-efficacy that was proposed by previous research (Fosse, Buch, Säfvenbom, & Martinussen, 2015).
In this study, the best predictor of high school academic achievement was middle school academic achievement which indicates that high school years are indicative of hard conscientious work, resilience and persistence (Lee, Baring, & Sta. Maria, 2016). As to personality traits, neuroticism was significantly related to high school academic achievement as well, given that students with high levels of neuroticism have developed better strategies in managing their own emotional responses (O'Connor & Paunonen, 2007; Poropat, 2009). On the other hand, conscientiousness was significantly related to high school academic achievement probably because those students that are organized, disciplined, skilled and are accomplishment oriented perform better in academic tasks when compared to students without these personal characteristics (Tomas & Adrian, 2003).
As to self-efficacy, extraversion is a significant predictor given that as it increases, peer positive reactions may raise self-efficacy levels with it. Academic self-concept is also significantly related to self-efficacy as it provides a cognitive base upon which students develop their academic self-efficacy beliefs (Bong & Skaalvik, 2003).
The transition from middle to high school is a challenging time for adolescents. Not only are adolescents dealing with a real change to a new school, but are also handling maturity, education as well as new interpersonal challenges that affect academic achievement (Leeson, Ciarrochi, & Heaven, 2008). Currently in the Mexican public education system there is no influence that motivates and aids personality regulation in these adolescents or aids them in their adaptation process, which is why the Mexican education system in close cooperation to families should improve the motivational factors to obtain better results in the future (Ruiz, Contreras, & Oliver, 2017).
Conclusion
This study contributes to the knowledge of high school academic achievement and its relation with certain psychological factors through the comparison of three conceptual models that consist of the following: Personality traits (HEXACO), self-efficacy in academic achievement (Stajkovic et al., 2018), academic self-concept and middle school academic achievement in Mexican public high school students. The results show that these factors can also help define the student’s profile once they enroll in high school, which would result in lower rates of academic failure as well as helping students develop the necessary abilities for a successful experience in middle and high school. Students may use the strength of the beliefs of their own self-efficacy in order to help themselves remain in school and boost their previously acquired aptitudes and knowledge.
The findings of this study can aid in the development of new study plans and syllabi in high school, it is advisable to develop certain psychological aspects that will in turn improve high school academic achievement. This information can also be used to inform high schools about the importance of middle school GPA when they are admitting students.
As to further directions, we would suggest the addition of stronger correlates to high school academic achievement such as self-control (Duckworth, Taxer, Eskreis-Winkler, Galla, & Gross, 2019) in order to increase explanatory power. Although we do not doubt the veracity of student-reported GPA, having access to the institution’s records would be more convenient as this data would allow testing for subject/area academic achievement instead of global academic achievement. For future investigations, the sample could be composed differently or subdivided as further comparisons between shifts, or semesters might provide valuable insights on achievement. Additionally, it would be useful to have experimental data on how easily cognitions and capabilities can change in adolescents, by different periods of time and due to different circumstances in order to answer the question: To what extent do these changes impact GPA? On the other hand, theory based interventions might help students to optimize their potential to reach their desired levels of academic achievement.











 nueva página del texto (beta)
nueva página del texto (beta)


